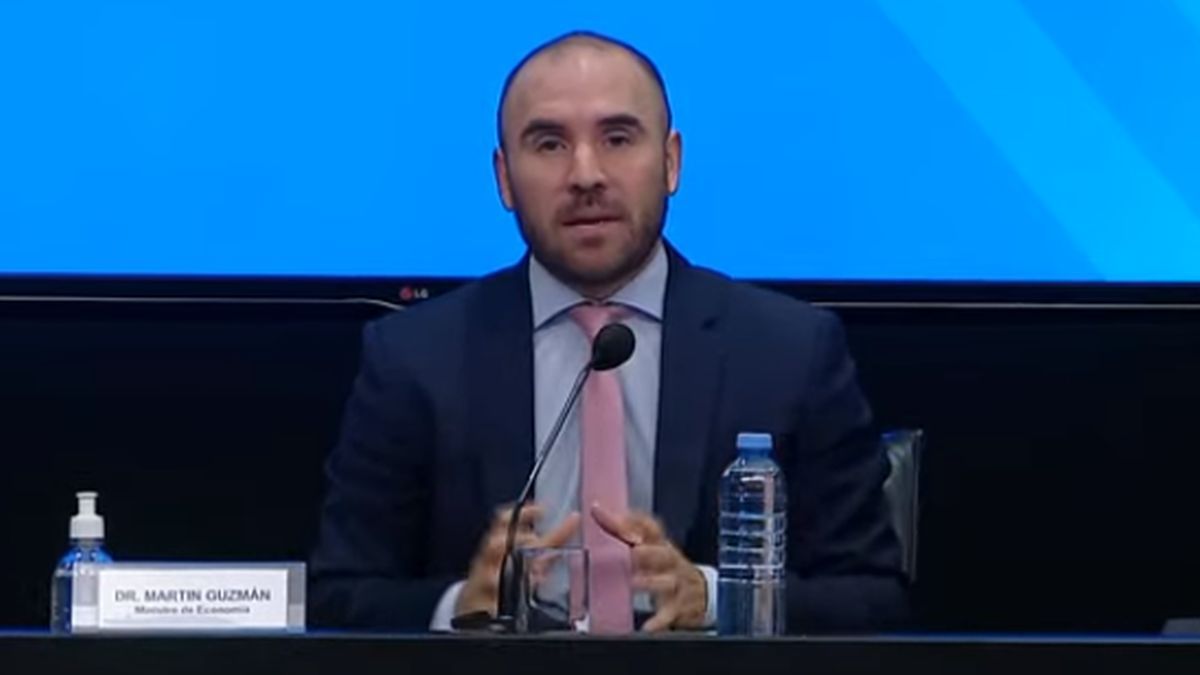
The agreement, finally, will not be a ten-year Extended Fund Facility (EFF) but rather It will be a two and a half year program, of the Stand By type, like the one signed by the government of Mauricio Macri in 2018.
“The agreement was to be able to have a fiscal policy that does not inhibit recovery, with spending growing moderately, that is, it was achieved without adjustment policies. And a fiscal correction was proposed: for the year 2022 a deficit of 2.5%; in 2023 it will be 1.9% and in 2024 it will be 0.9%”, said Guzmán at a press conference. And he added: “To target the tax reduction, the tax administration will be strengthened to reduce evasion and money laundering.”
Regarding the monetary program, he said: “There will be a gradual reduction in the Central Bank’s assistance to the Treasury; in 2021 it was 3.7%; in 2022 it is aimed at being 1%; in 2023 0.6% and in 2024 it is close to zero. And converge to a situation in which there is no more systematic financing”, he specified. “The idea is to have a structure of positive real interest rates to have greater financial and exchange stability,” he assured.
Regarding inflation, he reiterated that it is a “multicausal” phenomenon, with a fiscal-monetary scheme and “strengthening public finances with a gradual reduction of the fiscal deficit.” Fourth, “the State will fulfill a role of anchoring expectations, for that the role of price and income agreements in the anti-inflationary scheme.” “There will be no exchange rate jump, but a policy of accumulation of international reserves, of USD 5 billion in 2022.”
The details of the agreement with the IMF
- Argentina was able to reach a policy agreement with the IMF without adjustment policies.
- The agreement was to have a fiscal policy that does not inhibit the continuity of the recovery.
- All the rights of our retirees will be maintained, there is no labor reform, there is no privatization of public companies.
- It is proposed that there be a gradual reduction of the fiscal deficit on the basis of a recovering economy.
- For the year 2022, a primary fiscal deficit of 2.5% of GDP is projected and for the year 2023 this variable takes the value of 1.9%; and for 2024 of 0.9%.
- It is pointed out that in 2022 the monetary financing will be 1% of the Product; in 2023 around 0.6% and in 2024 it will be close to 0 and be able to converge in a situation in which there is no more systematic financing from the Central Bank to the Treasury.
- There will be no exchange rate. The exchange rate policy will continue in the line in which it has been carried out.
- A framework was agreed upon that aims to have a structure of real interest rates that results in positive values.
- Price agreements are going to have an important role and space in the inflation scheme.
- Financing has been negotiated for an amount equivalent to the amount of what was the standby program that the previous government had agreed to. That is, around 44.5 billion dollars.
- I invite everyone to accompany this process and I also invite the opposition. The program will be more robust if the social and political support is broader.
- The previous administration decided to go to the IMF and agreed to what was the record loan amount in the history of the institution: 57,000 million dollars, of which almost 45,000 million dollars were disbursed. That program resulted in a profound failure and deterioration of the economic and social situation in Argentina.
- The IMF itself, in the evaluation that it published a few weeks ago on such a program, recognized that the program failed, that it failed to achieve any of the objectives that it had set itself, both in the economic sphere, as well as in the social sphere, and in the financial.
- What we proposed throughout the course of the negotiations was to have the support to be able to refinance that debt of 44,500 million dollars without undermining the development opportunities of our Nation, being able to continue on the path of the strong economic recovery that Argentina is experiencing. , with possibilities of more job creation, more production, more value added and more stability. That is, to be able to continue building a calmer economy.
- We were able to reach an understanding on the macroeconomic framework and key policies for a new program with the IMF.
- This general framework has two blocks: on the one hand, the scheme of macroeconomic policies. On the other hand, the so-called measures that promote medium-term growth and lasting stability.
- From the macroeconomic point of view there are four blocks: the first block is the fiscal one. The agreement was to have a fiscal policy that does not inhibit the continuity of the recovery. The State will be able to play a moderately expansive role with spending in real terms growing moderately.
- Argentina was able to reach a policy agreement with the IMF without adjustment policies.
- It is proposed that there be a gradual reduction of the fiscal deficit on the basis of a recovering economy.
- For the year 2022, a primary fiscal deficit of 2.5% of GDP is projected and for the year 2023 this variable takes the value of 1.9%; and for 2024 of 0.9%.
- There will be a greater targeting of State resources and a greater expansion of public investment that Argentina so badly needs to generate more productive capacity and for the private sector to be in a position to give rise to more vibrant activity. The Science and Technology Financing Law will also be respected.
- Work will be done to strengthen the tax administration seeking to attack the evasion problems that have existed in Argentina, especially in the segment with the highest contribution, and also to have measures to attack money laundering problems.
- The second block in the macroeconomic is the monetary and financial. There is going to be a gradual but decisive reduction in the monetary assistance provided by the Central Bank to the Treasury.
- In 2021, monetary financing to the Treasury ended at around 3.7 points of GDP, which was a substantial reduction compared to 7.3 points in the worst year of the pandemic.
- It is pointed out that in 2022 the monetary financing will be 1% of the Product; in 2023 around 0.6% and in 2024 it is close to 0 and to be able to converge in a situation in which there is no more systematic financing from the Central Bank to the Treasury but in a more normalized economy, the money supply can move from one consistent with the evolution of the demand for our currency without this entailing additional pressures on the exchange rate and therefore on inflation.
- A framework was agreed that aims to have a real interest rate structure that results in positive values in order to strengthen the demand for assets in our currency and contribute to exchange and financial stability.
- On the financial front, work will continue to rebuild the public debt market in local currency.
- A comprehensive approach was agreed upon, based on the premise that inflation is a multi-causal phenomenon.
- First of all, there is a factor that is productive; has been the historical inability of Argentina to be able to have a sustained growth of exports that allows that when the country grows and therefore the demand for foreign currency grows, the foreign currency can be counted on so that the growth continues and we do not collide with problem of lack of reservations.
- There is a set of policies that aim to promote the development of sectors that have the capacity to generate foreign currency in our economy.
- Second, what we need is to continue improving the financing profile of public policy and strengthening the sustainability of public finances.
- Third, there is the monetary policy that is based on aiming for a structure of positive real interest rates.*
- Fourth, there is the coordinating role that the State plays to anchor expectations. For this, the role of price and income policies is fundamental.
- Price agreements are going to have an important role and space in the inflation scheme.
- There will be no exchange rate. The exchange rate policy will continue in the line in which it has been carried out.
- An objective of accumulation of international reserves is proposed. A goal is set for 2022 of growth in international reserves of 5,000 million dollars.
- There will continue to be regulations in the financial account that prevent Argentina from going through a situation of instability.
- It points to a horizon of macroprudential regulations such that the outflow of speculative capital is discouraged.
- All the rights of our retirees will be maintained, there is no labor reform, there is no privatization of public companies.
- The scheme of measures that promote growth aim to solve the problems that our productive structure has been suffering. This agreement will allow growth to continue in Argentina and economic and social objectives to be addressed.
- We ended up in a reasonable place where we had to compare between two alternatives: one alternative was a leap into the unknown, into uncertainty, with no guarantees of anything. This other alternative makes it possible to provide more predictability, more certainty and leave a place that would have been a place of anguish for millions of Argentine men and women. It is an alternative that is reasonable.
- The best agreement that could be achieved was reached and the President of the Nation made the decision to give this peace of mind to the Argentine men and women. It allows us to take other steps to build an Argentina with more work, more production and better conditions of stability in each of them.
- The program will have a duration of 2 and a half years and there is still work to be done on the economic and financial policy memorandums between the National Government and the IMF. This is going to take a few weeks. They will write based on what has already been agreed upon.
- Financing has been negotiated for an amount equivalent to the amount of what was the standby program that the previous government had agreed to. That is, around 44.5 billion dollars. Everything that remains is due between now and the completion of the standby program payments plus the amount of capital amortizations already made in September and December 2021 that were paid with the SDRs that Argentina had received during the past year.
- There will be reviews and in each of them, disbursements. With these disbursements, the payments of the program agreed upon by the previous government will be made and the remainder will be used to accumulate reserves.
- At all times, our President maintained his course, calm and the ability to negotiate with all his strength and lucidity, defending the interests of our Nation. This result is mainly responsible for our President, also our Vice President Cristina Fernández de Kirchner, owner of a unique force that has also been of great value for what has been achieved. And to the president of the Chamber of Deputies, Sergio Massa, who has been very active, helping a lot, especially in this final stretch, which are the most critical and delicate moments, both nationally and internationally.
- I invite everyone to accompany this process and I also invite the opposition. The program will be more robust if the social and political support is broader.
Source From: Ambito
David William is a talented author who has made a name for himself in the world of writing. He is a professional author who writes on a wide range of topics, from general interest to opinion news. David is currently working as a writer at 24 hours worlds where he brings his unique perspective and in-depth research to his articles, making them both informative and engaging.