As individuals, there are steps we can take to reduce our exposure to microplastics. I know the details.
In the constant search to understand the effects of environmental pollution in the Human healththe scientists They discovered that the microscopic plasticsinvisible to the naked eye, infiltrated practically every corner of the bodyeven reaching our brain.
The content you want to access is exclusive to subscribers.
The omnipresence of these fragments It is not a coincidence. From the water that we drink until air that we breathe, microplastics They became integrated into our daily environment. Its presence in the oceans, land and atmosphere created a global network that inevitably exposes us to its influence, penetrating our food chain and ultimately in our organism.


brain.jpg

The buildup of these plastic particles inside the brain raises crucial questions about long-term brain health. How do these materials affect cognitive function? Can they trigger or accelerate the development of neurodegenerative diseases?
Freepik.
Microplastics in your brain: what science says
Scientists are still unraveling the precise mechanisms of how microplastics affect the brainbut the similarities in the accumulation of certain proteins associated with neurodegenerative diseasesAs the Alzheimer’s and the Parkinson’sset off alarms in the global community.
“At the research level we are practically facing a blank page“warned the neuroscientist of the University of Rhode Island, Jamie Rossa specialist in helping to answer what causes Parkinson’s in cases where there is no genetic predisposition on the part of the sufferer.
Plastics in the sea.jpg

Accumulation of plastics in the sea.
The world
Plastic in the brain: how it was discovered
Ross led several experiments tested in micein which he made them drink water with microplastics containing markers for three weeks. After that, they discovered that these particles cross the blood-brain barrier of the brainproduce on him an effect similar to that of the dementiasand manifest similar alterations to those who suffer from them.
Although information is not abundant so far, researchers warn that There is concrete evidence about the damage caused by the material and that we should avoid using it if it is not excessively necessary.
mice
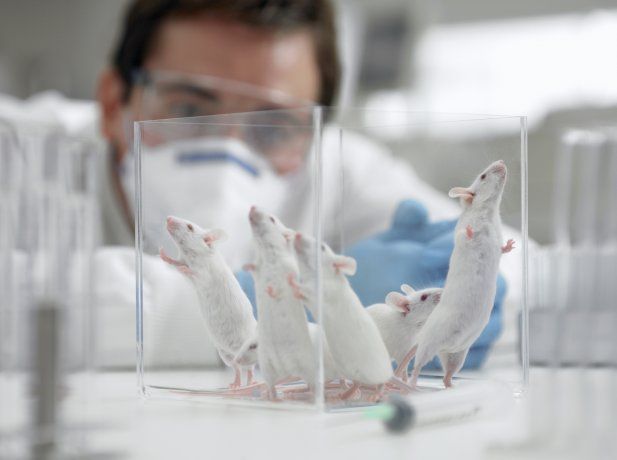

Not only in our brain, but also in a large part of the body.
A study of the Newcastle Universityin Australiacalculated that each week an average of 5 grams of plasticthe equivalent of a credit card. Ingestion occurs through what we consume or the air we breathe.
His presence could be observed in the placentathe breastmilkhe lunghe liverhe spleenthe kidneysthe blood. Researchers call them microplastics when its diameter is less than 5 millimeters (mm) and nanoplastics when it is less than 0.001 mm.
Source: Ambito
I am an author and journalist who has worked in the entertainment industry for over a decade. I currently work as a news editor at a major news website, and my focus is on covering the latest trends in entertainment. I also write occasional pieces for other outlets, and have authored two books about the entertainment industry.