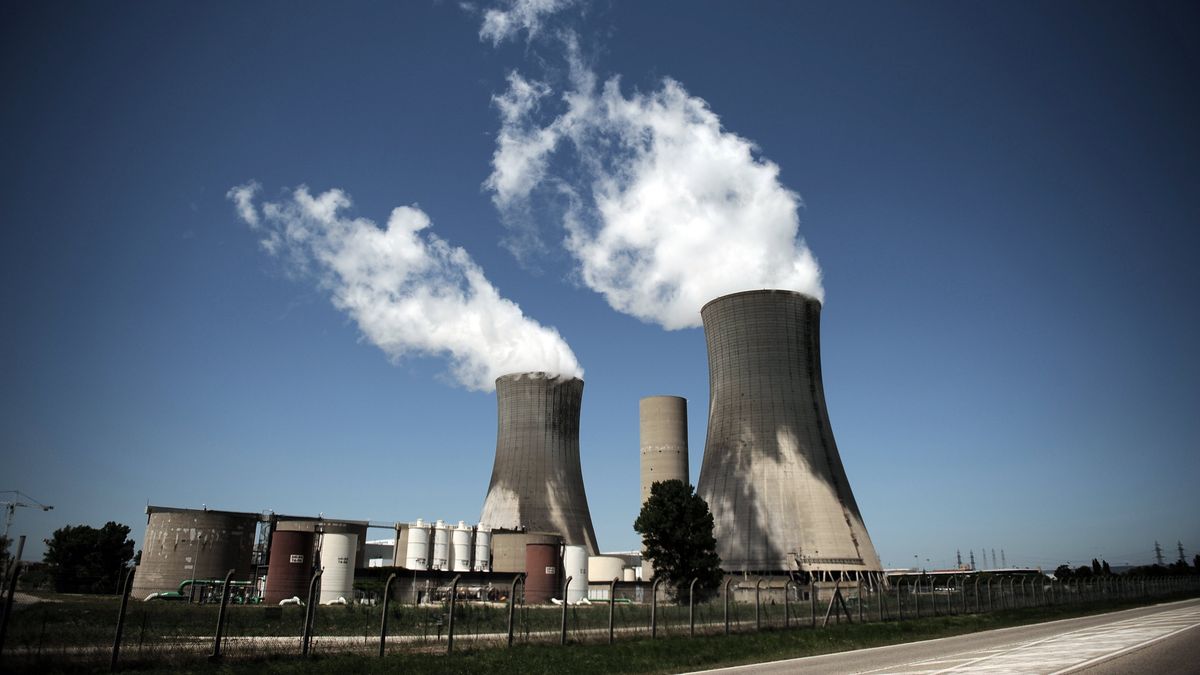
For much of the 20th century, nuclear energy was seen as a dangerous source and contrary to the nascent vision of sustainability. This stigma had clear foundations: its high technical complexity, the problematic management of radioactive waste, and historical disasters that left deep social and environmental traces. However, in recent years, The perception of nuclear energy has taken a significant turn. In a context of growing energy demand driven by artificial intelligence (AI) and the urgency to decarbonize economies, this source has reemerged as a key pillar on the path to a clean energy future.
In this framework, Argentina, with its vast nuclear history, could benefit enormously. The country has a unique history in the development and management of nuclear technology, which could attract the attention of large technology companies such as Amazon, Google and Microsoft, which are betting and investing in nuclear reactors to power their multiple data centers.
Along these lines, it is important to understand how nuclear energy works, which is generated through fission, a process in which the nuclei of heavy atoms split, releasing large amounts of thermal energy. This energy is used to produce electricity through mechanical generators (turbines). From fission, it is a process similar to that used to generate electricity from the heat of fossil fuels such as coal, gas and oil.
Since the creation of the first power plants in the 1950s, nuclear energy has been a key player in the global energy matrix, although its history is marked by two major disasters: Chernobyl (1986) and Fukushima (2010). Both with environmental consequences, deaths and long-term illnesses that deeply marked her in reputational terms. It should be noted that these events promoted substantial advances in safety and efficiency in the industry, making it mature and evolve exponentially.
In this sense, an example is the development of Small Modular Reactors (SMRs), which offer a safer, economical and adaptable alternative for the generation of electricity with low carbon emissions. According to the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA), these innovations are revolutionizing the nuclear sector and minimizing environmental risks.
Therefore, within the framework of an economic and productive system that is making great efforts to transition towards decarbonization, the great attraction of nuclear energy is its ability to produce electricity on a large scale without emitting greenhouse gases. Unlike renewable energies, such as wind and solar, which depend on climate and geographical conditions, nuclear can generate continuously, which is crucial to meet the growing energy demand not only of our cities, but also of data centers and artificial intelligence (AI) applications, which require a constant and predictable high supply. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), nuclear power already generates more carbon-free electricity than wind and solar combined, and installed capacity is expected to triple by 2050, helping to achieve the world’s zero-emissions goals. great powers and corporations at a global level.
As energy demand grows due to the advancement of AI and the needs of data centers, leading companies have decided to bet on this technology. Amazon Web Services (AWS), for example, announced this year an investment of $500 million to develop this type of new reactors. In the case of Microsoft, it plans to reactivate a reactor in the US to allocate its energy production exclusively to its AI centers. Google, for its part, signed the world’s first corporate agreement to purchase nuclear power from multiple small modular reactors (SMR). The company says this will help them achieve their ambitious carbon-free energy and net zero emissions goals. Other companies such as OpenAI are also evaluating this technology to solve their energy needs.
This thirst for clean energy can be beneficial for the country, which has more than 50 years of productive history, top-level qualified professionals and three operational nuclear power plants: Atucha I, Atucha II and Embalse. The Atucha I Nuclear Power Plant has been providing energy to Argentina since 1974 and is the first nuclear power plant in Latin America. Beyond the infrastructure and its operation, the expertise in terms of research and development of the National Atomic Energy Commission and INVAP, a company that has exported nuclear reactors and promotes cutting-edge technology, are fundamental assets for this new energy stage that is poses the world.
Logically, its growth is not without challenges. Those related to the management of radioactive waste are among the priorities, but technological advances allow us to see that it is possible to manage them effectively and sustainably.
Last year, at the highest environmental meeting of political leaders, COP28 held in Dubai, 24 countries committed to tripling installed nuclear power by 2050 to achieve a net zero emissions balance on that horizon. This year, At COP29 held in Baku, Azerbaijan, the number of signatories of this agreement expanded to 31, including powers such as the United Kingdom, France, Canada and the United States.
Thus, nuclear energy seeks to position itself as a safe, clean and reliable option for the global energy transition. While its risks should not be minimized, technological advances and increased demand for clean energy suggest that this source may be indispensable in the fight against climate change. As more companies and governments bet on this supply, nuclear energy has the potential to transform its image and position itself as a key piece in the construction of a sustainable future. A trend that Argentina, given its capabilities and potential, must take advantage of.
Managing Partner at Business & Sustainability
Source: Ambito
I am an author and journalist who has worked in the entertainment industry for over a decade. I currently work as a news editor at a major news website, and my focus is on covering the latest trends in entertainment. I also write occasional pieces for other outlets, and have authored two books about the entertainment industry.