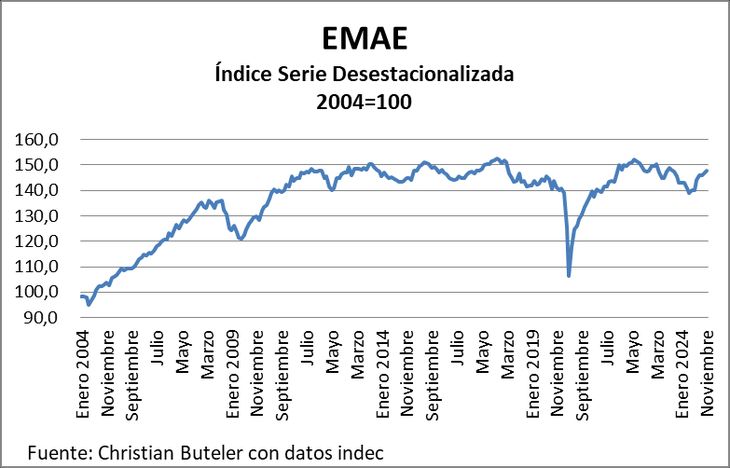
The recent report of the monthly Economic Activity Estimator (EMAE) corresponding to November, published last week, provides an updated framework on the dynamics of the Argentine economy. According to the data, the EMAE registered An interannual increase of 0.1% and a unstacted monthly rise of 0.9%. These numbers suggest a general recovery in the index, but a more detailed analysis reveals deep disparities between the sectors that make up economic activity.
DESESTATIONALIZED SERIES INDEX.JPG
Source: Christian Buteler with INDEC data.
General recovery, but with nuances
The general index of the EMAE managed to recover the entire fall experienced during the first months of the management of President Javier Milei, after touching a minimum of 139 points in April last year. This brand’s rebound A milestone after a descending trend that began in March 2023accentuated by measures such as the devaluation of the currency and a strong contraction of public spending.
The Government has declared overcome the recession initiated in early 2024, highlighting the recovery of the values prior to November 2023. Although this is technically correct, A more detailed sector inspection shows significant heterogeneity in the results.
Sectors with opposite trajectories
EMAE broken down economic activity in 16 sectors, of which only 6 show a positive year -on -year growth:
- Fishing: +164.6%
- Financial intermediation: +9.9%
- Exploitation of mines and quarries: +7.1%
- Net taxes: +3.7%
- Teaching: +1.1%
- Real estate activity: +0.9%
In contrast, sectors that face notable contractions include:
- Construction: -14.2%
- Electricity, Gas and Water: -5.6%
- Manufacturing industry: -23%
- Trade: -1.3%
While the general index shows recovery signs, These sectoral results expose an unequal dynamic. The sectors with the greatest falls coincide with those that generate the most employment, which explains why the benefits of this recovery do not feel widely in the social and labor spheres.
A fragile recovery
By extending the analysis horizon to the period prior to the adjustment policies implemented by the current government, the structural challenges of the economy become more evident. Between March 2023, when the de -stationalized index reached its peak of 150.4 points, and November 2024, EMAE accumulated a 1.7% drop. This decrease is especially pronounced in key sectors:
- Manufacturing industry: -6.8%
- Construction: -27.4%
- Trade: -16.0%
Economic Activity.jpg
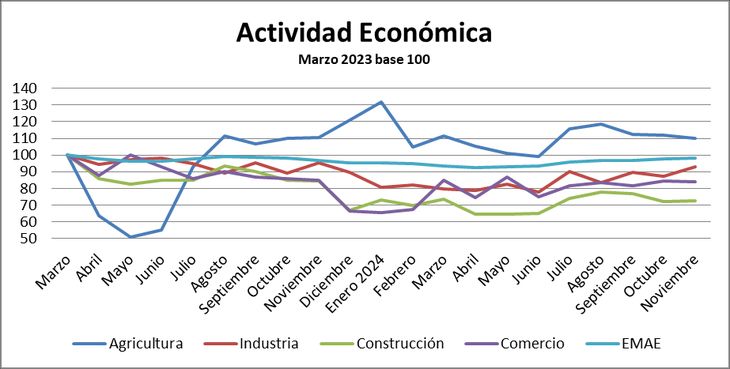
Source: Christian Buter with INDEC data.
On the other hand, agriculture showed a significant growth of 10.2%, an expected fact after the drought of 2023.
Perspectives and challenges
The Argentine economic panorama remains uncertain, marked by a technical recovery that lacks structural solidity. The disparity between sectors raises questions about growth sustainability. Besides, factors such as backward exchange rate and import competition They could generate new pressures that limit economic performance.
To consolidate a more inclusive recovery, It will be essential to implement policies that promote activity in employment intensive sectors and promote productive investment. Otherwise, growth could remain limited to a small number of sectors, exacerbating existing gaps.
Conclusion
While EMAE’s general figures indicate an advance towards recovery, sector heterogeneity evidences a fragmented economy. The immediate challenge lies in Transform this unequal recovery into sustainable and equitable growth, capable of strengthening both investor trust and the well -being of the population.
Source: Ambito
I am an author and journalist who has worked in the entertainment industry for over a decade. I currently work as a news editor at a major news website, and my focus is on covering the latest trends in entertainment. I also write occasional pieces for other outlets, and have authored two books about the entertainment industry.