Menu
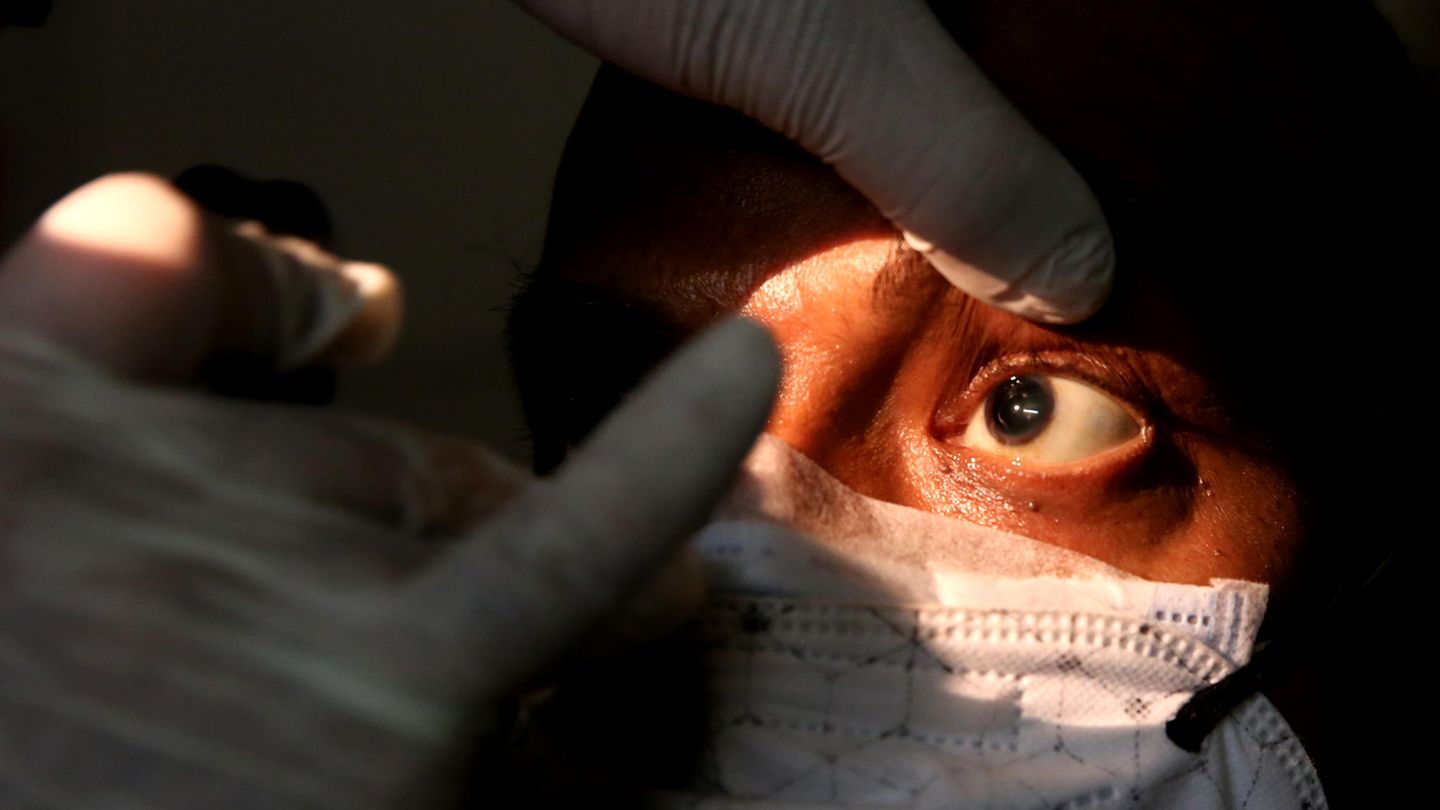
Corona: What is known about infections with the “black fungus”
Categories
Most Read
Wash your hands properly: You should know these facts and myths
October 15, 2025
No Comments
Shaping your eyebrows: This is how you give your face more expression
October 14, 2025
No Comments
Happiness Research: Are Young Adults Unhappier Than Before?
October 14, 2025
No Comments
Assets: How to Protect Grandma’s House and Belongings
October 13, 2025
No Comments
Time change again: Why hasn’t it been abolished yet?
October 13, 2025
No Comments
Latest Posts

While Milei waits for an announcement, Donald Trump opens negotiations with Lula da Silva over tariffs on Brazil
October 16, 2025
No Comments
While the government of Javier Milei looking forward to an official announcement USA about a trade agreement, the Brazilian president, Luiz Inácio Lula da Silvareported

Autobiography: Britney Spears’ ex-husband raises alarm in memoir
October 16, 2025
No Comments
Lisa HarrisI am an author and journalist who has worked in the entertainment industry for over a decade. I currently work as a news editor

Forget about boring exercises: effective and dynamic training for older adults
October 16, 2025
No Comments
October 15, 2025 – 9:30 p.m. A fun and recreational activity that also serves to work all the muscles of the body at the same
24 Hours Worlds is a comprehensive source of instant world current affairs, offering up-to-the-minute coverage of breaking news and events from around the globe. With a team of experienced journalists and experts on hand 24/7.