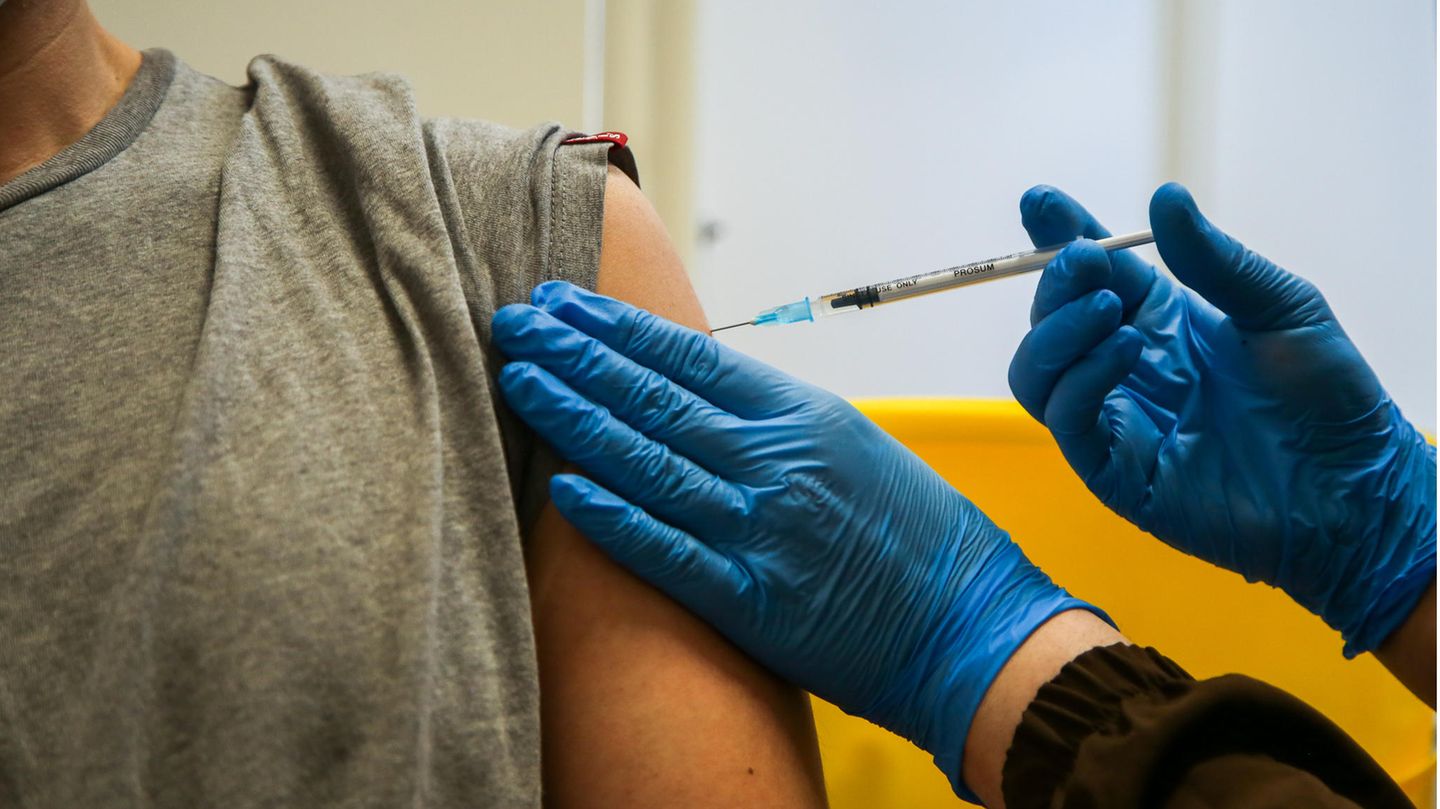
After a vaccination against the coronavirus, heart muscle inflammation can occur in rare cases – this is already known. A study now shows: The risk from Covid-19 is greater.
Slight pain at the injection site, headache or tiredness: Most people develop only mild or hardly noticeable vaccination reactions after a corona vaccination, which quickly subside.
After vaccinations with the so-called mRNA vaccines (Biontech / Pfizer and Moderna), however, heart muscle inflammations are also observed occasionally. The rare cases of myocarditis concern and occur slightly more frequently after the second dose than after the first. Most of those affected recover quickly and completely from their symptoms.
A large study with data from Israel provides new insights on the topic and puts the risk in relation again: According to this, Covid disease increases the risk of myocarditis more than vaccination. Doctors had suspected this for a long time based on clinical experience. The study, which appeared in the journal “” (NEJM) this week, supports the observations.
The study included data from more than 1.7 million people – half were vaccinated against the coronavirus, the other half unvaccinated. The people were at least 16 years old. The corona vaccine from Biontech / Pfizer is used in Israel. The results of the study therefore relate exclusively to this vaccine.
The researchers calculated the frequency of 25 different adverse events. How often did they occur in each group?
Myocarditis risk compared
It was found that the overall risk of myocarditis was low, but – as expected – occurred somewhat more frequently in the vaccinated group than in the non-vaccinated group. The plus was 2.7 cases per 100,000 people. The mean age of the 21 vaccinated subjects who developed myocarditis was 25 years. Mostly men were affected (90.9 percent).
The researchers then compared the data from infected and non-infected people. They compared 170,000 Covid 19 patients with a control group who had not been infected with the virus. It showed that the risk of myocarditis was significantly greater among those infected. The plus in this group was eleven additional cases of myocardial inflammation per 100,000 people.
In an interview with the “New York Times”, Ben Reis, one of the co-authors of the study, referred to the dangers of Covid-19: People who had previously postponed the vaccination for fear of myocarditis would have a Reiser, who conducts research at Harvard Medical School, stressed, that they are at higher risk for that adverse event if they are not vaccinated and become infected.
Corona vaccination “safer” than infection
In addition to the risk of myocarditis, the researchers listed other complications related to Covid disease: Sick people were therefore at an increased risk of heart attacks, cardiac arrhythmias and blood clots in the lungs or thrombosis. For example, for every 100,000 infections there were 25 additional heart attacks and 62 cases of pulmonary embolism.
This did not apply to the vaccinated group. However, swollen lymph nodes, cases of shingles or appendicitis were observed somewhat more frequently. The risk for the last two diseases was only slightly increased, however. “The corona vaccination is safer than the infection,” said Carsten Watzl, Secretary General of the German Society for Immunology eV, summarizing the results of the study
However, the age restriction of the study must be taken into account: children and adolescents under 16 years of age were not examined. It is already known that adolescents and young men are most likely to develop rare myocarditis after vaccination.
The Standing Vaccination Commission (Stiko) Accordingly, the benefits of the vaccination outweigh the possible risks in this age group. The Stiko points out, among other things, that the inflammation also occurs with Covid-19 diseases and that the majority of the affected patients have an uncomplicated course.