Menu
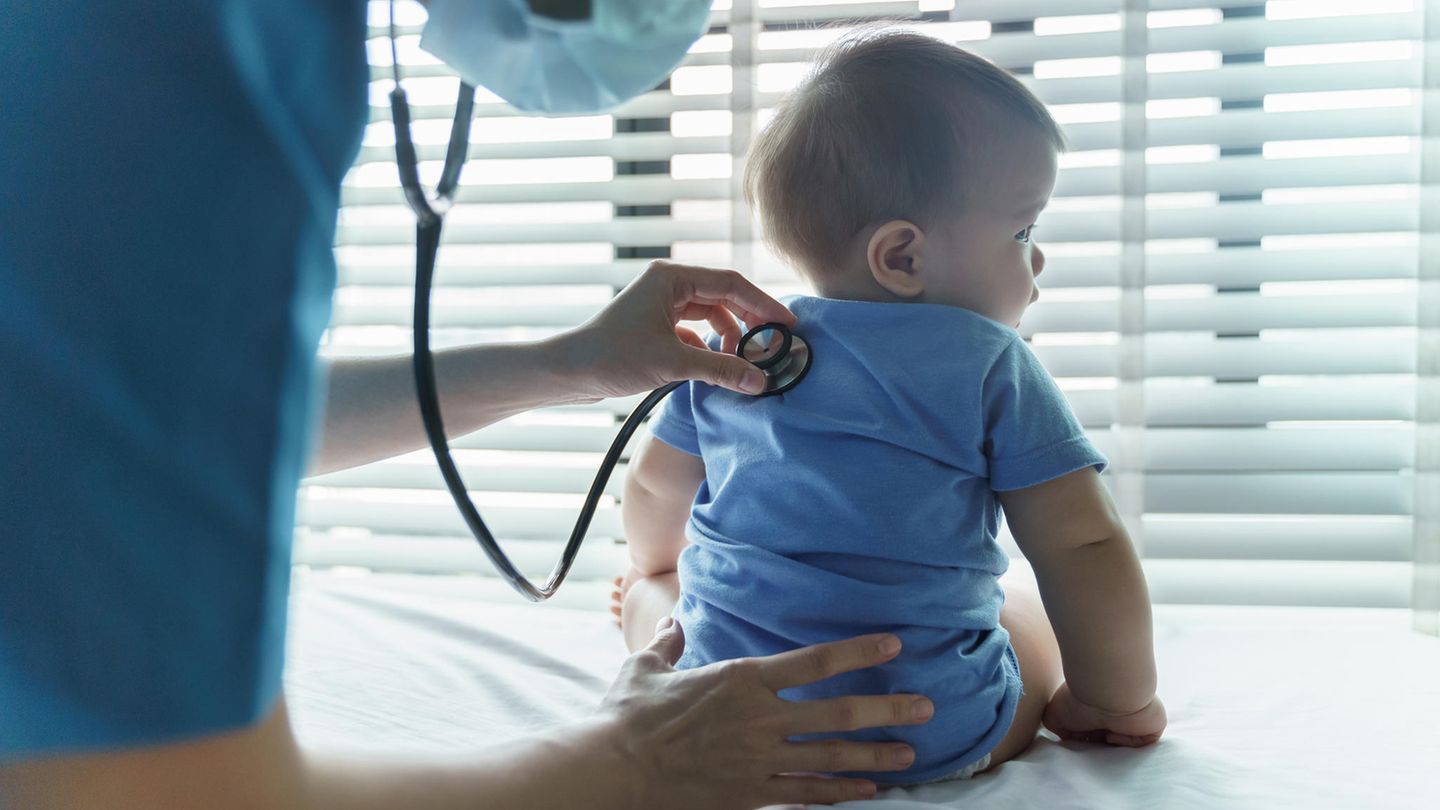
RS virus: when parents should take their children to the doctor
Categories
Most Read
Nivea Advent calendar in the test: This is behind the 24 doors
October 6, 2025
No Comments
Bath bombs in trend: tips for effect & application
October 6, 2025
No Comments
Emigration: Babette’s new beginning in Copenhagen changed her life completely
October 6, 2025
No Comments
Building freezing: These animals stop entire construction sites
October 4, 2025
No Comments
People’s fatigue and fever: could it be Lyme disease?
October 4, 2025
No Comments
Latest Posts

With the new CPI, registered salaries accumulate a real drop of 11% under the management of Javier Milei
October 6, 2025
No Comments
October 6, 2025 – 17:50 While the private sector has mostly ironed against November 2023, the strong adjustment is made on public employees who lose
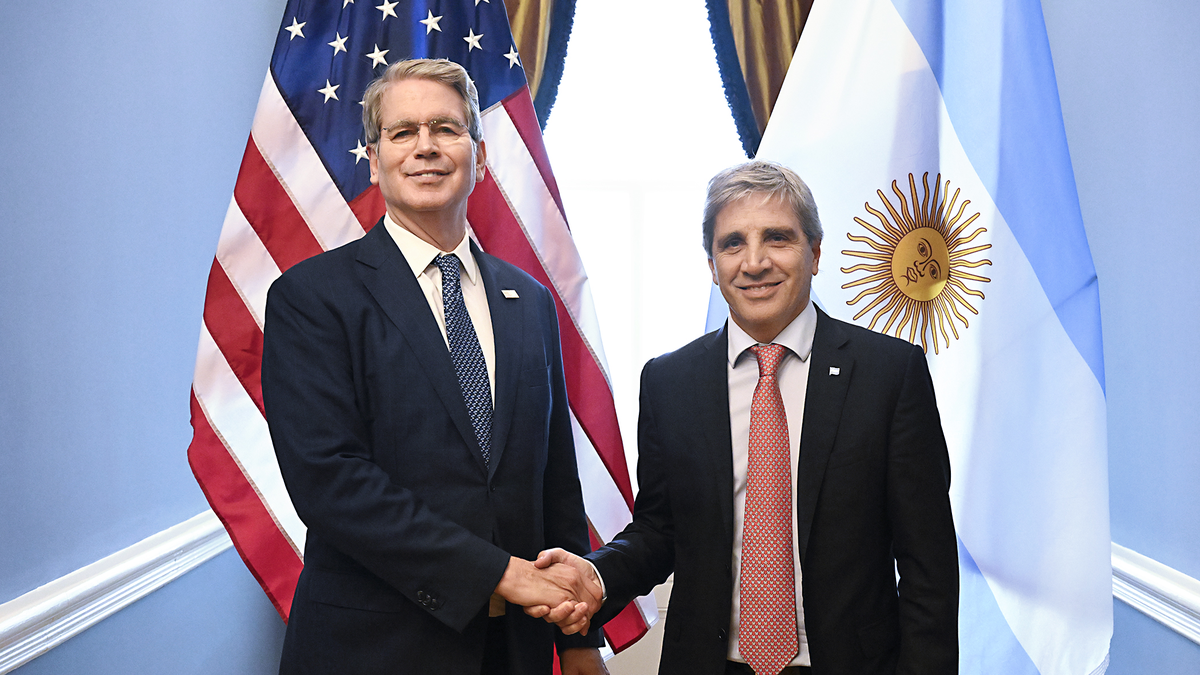

They discussed details of financial salvage
October 6, 2025
No Comments
October 6, 2025 – 17:46 The US Treasury Secretary Scott Besent, once again used his social networks, in this case, to welcome the Minister of
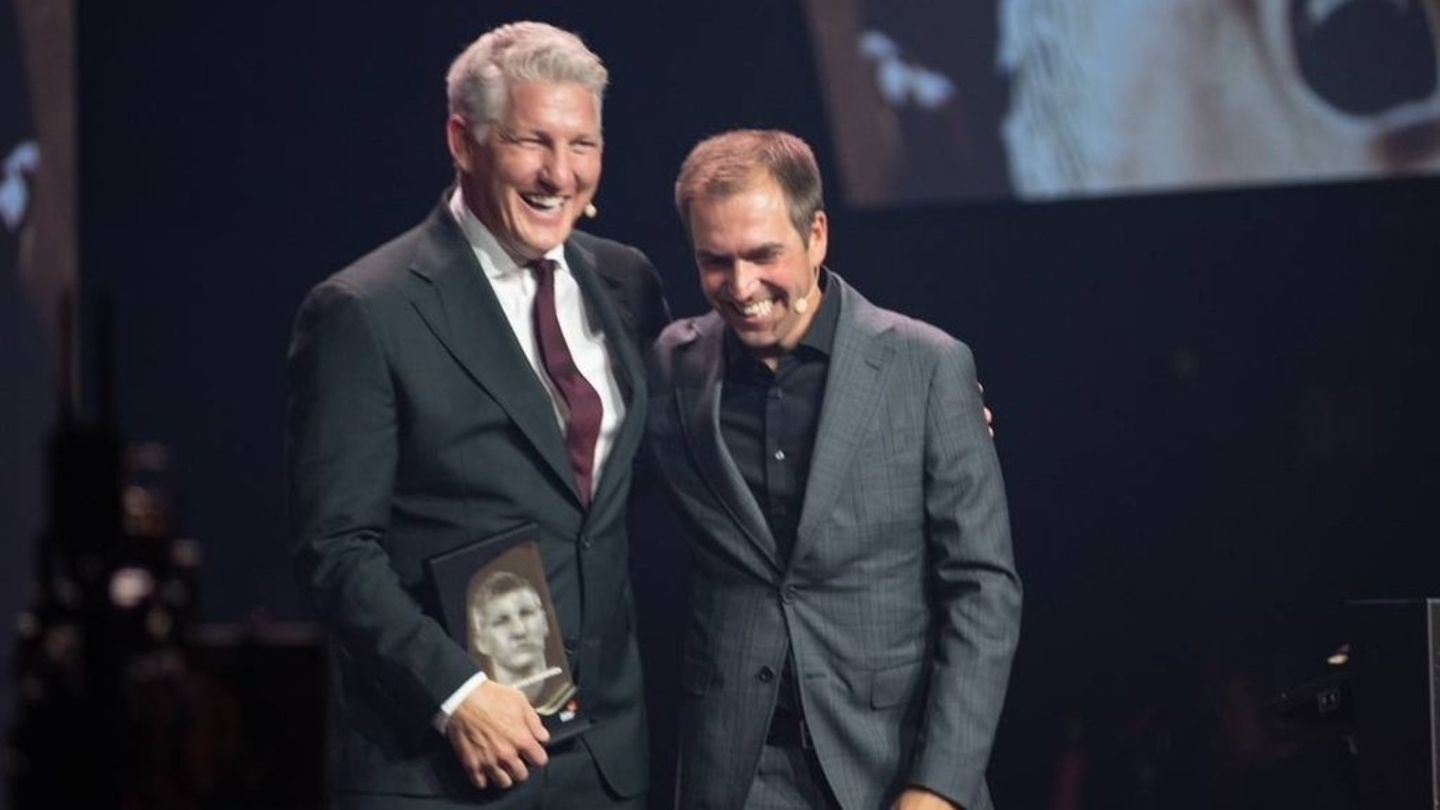

Hall of Fame of German Football: Schweinsteiger recorded in fame hall
October 6, 2025
No Comments
Lisa HarrisI am an author and journalist who has worked in the entertainment industry for over a decade. I currently work as a news editor
24 Hours Worlds is a comprehensive source of instant world current affairs, offering up-to-the-minute coverage of breaking news and events from around the globe. With a team of experienced journalists and experts on hand 24/7.