Berliner with 66 mother
Being a mother late – is that just risky or even advantage?
Copy the current link
Add to the memorial list
The late motherhood is trendy. Some wait with the first child until they are 40 or 50. How dangerous is that? And what speaks for it?
At the age of 66, one has become one. It is your tenth child. It was converted, she says, naturally. The norm is by no means. Because the fertility of women decreases significantly from the age of 35. From the age of 50, the likelihood of becoming pregnant decreases according to the professional association of gynecologists. Nevertheless, the trend has been going to the late motherhood for years.
While the average age of women in the first child was a good 25 years in 1980, it has now risen to over 30. This is also possible through medical progress. It is not without risk. The health risks grow with the age of the mother. A late motherhood can also bring advantages. An overview.
How likely is it to be late?
The likelihood of becoming pregnant in the twenties is around 25 percent. From the age of 30, the chance has dropped to 15 percent, from 40 the probability is only around 5 percent. From 50 it tends to zero.
Medical progress – artificial fertilization, surrogacy, frozen egg cells, egg donation – makes it possible that women can still become a mother even in the advanced age beyond 50. Spontaneous pregnancies are unlikely at this age, but not impossible. An example: The Chinese Tian Ying gave birth to a girl in 2019 at the age of 67. Ying is considered the oldest known mother of a naturally produced child.
What is the reason why fertility in women decreases with age?
Women are born with a reservoir of egg cells. Experts assume that the number of immature egg cells is around one million at that time. No further egg cells are produced after birth. At the beginning of puberty there are still around 500,000 of the egg cells.
The number of egg cells shrinks with increasing age, and their quality also decreases. The risk increases that egg cells have an abnormal number of chromosomes, in women from 35: the chance is over 50 percent. For over 40 year olds, even 60 to 80 percent. This also increases the likelihood that a child with disabilities will be born.
In one of 100 women, the egg reserve even used up before the age of 40.
Does the lifestyle have an impact on reproductive ability?
“The later pregnancy is planned, the more important the physical health of women and their lifestyle”, can be found on the website of the gynecologist’s website. If you eat healthy, move regularly and do without nicotine, you have good chances of getting pregnant without any problems. Factors such as: stress, little sleep, unhealthy nutrition, alcohol and nicotine are considered to be detrimental to health and terribility.
When is pregnancy a risk pregnancy?
If a woman is 35 or older at her first pregnancy, this is rated as a risk pregnancy and is medically supervised by a close -meshed manner. This also applies to pregnancies under the age of 18 and mothers over 40 that expect multi -in.
Pregnancies in which there is an increased danger to the health and life of mother and child. In classification, factors such as previous illnesses, former misconceptions or premature births, obesity, but also the age of the pregnant women play a role. In the twenties, the risk of complications in pregnancies is the lowest.
What are the risks for late mothers and their children?
The risk of pregnancy complications, malformations and illnesses increases with age. From 35, among other things, the risk of misconceptions, pregnancy diabetes, high blood pressure, undersupply of the placenta increases, growths in the uterus and chromosome changes. So the probability that a 40-year-old pregnant woman gets a child with a Down syndrome, at 1 to 100. If the pregnant is 35, the probability is 1 to 365; If it is 20, the number is 1 to 2000.
Halle Berry, Gisele Bündchen and Co.: These celebrities received children in their 40s
© avalon.red / imago images More 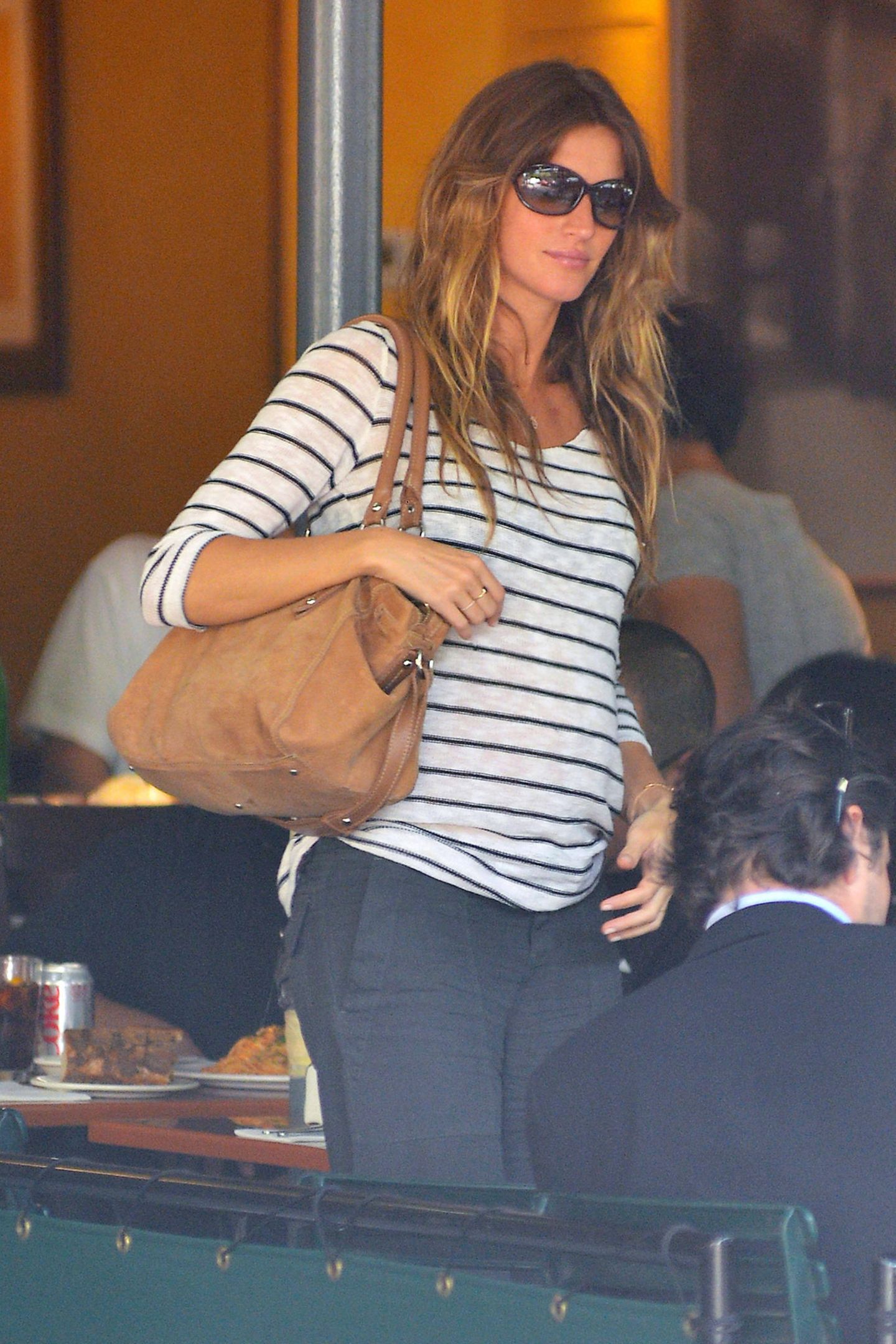
Open the image subtitle
Back
Further
Can late motherhood also have advantages?
A long-term study by the Max Planck Institute for Demographic Research suggests that a late pregnancy can also bring advantages. But the circumstances have to be right. The researchers argue that technical and social developments in western countries could compensate for the health risks of pregnancy in older age.
The results of the study also showed that the children of older mothers, which also applies to over 40-year-olds, were larger on average. They were also better at school, and the likelihood that the children visited a university was also higher than in children with younger mothers.
Source: Stern
I’m Caroline, a journalist and author for 24 Hours Worlds. I specialize in health-related news and stories, bringing real-world impact to readers across the globe. With my experience in journalism and writing in both print and online formats, I strive to provide reliable information that resonates with audiences from all walks of life.





