“The majority of cases are young men, self-identifying as men having sex with men. There is no death“, indicates the European agency based in Stockholm.
Outside of the 11 African countries where the disease is endemic, three countries currently concentrate the majority of confirmed cases: United Kingdom (71), the first country where unusual cases were detected in early May, Spain (51) and Portugal (37), according to the ECDC.
Europe concentrates the majority of cases with 191, of which 118 are located in EU countries. Canada (15), the United States (9), Australia (2), Israel (1), and the United Arab Emirates (1) are the non-European countries with cases.
It should be noted that suspected but unconfirmed cases were not included in the balance.
The total number of cases recorded by the ECDC has almost quintupled since its first report on May 20in which the agency indicated 38 cases, added AFP.
On Monday, in its first risk assessment, the ECDC considered the probability of contagion in the general population to be “very low” but that it was “high” in people with multiple sexual partners.
What does the WHO say about monkeypox?
the same day, The World Health Organization (WHO) confirmed an “atypical” situation but he judged it possible to stop the transmission of the disease between humans.
In turn, the WHO considered both “unacceptable and “inadmissible” the stigmatization of people for a diseaseregarding “messages that stigmatize certain groups” in the face of the monkeypox outbreak.
“It is unacceptable to stigmatize people because of a disease. Stigma is likely to only make things worse and prevent us from ending this outbreak as quickly as possible,” the UN health body said.
“We want to make it very clear that this is unacceptable… anyone who has close physical contact of any kind with someone with monkeypox is at riskregardless of who they are, what they do, who they choose to have sex with or any other factor,” he added, on the UN website.
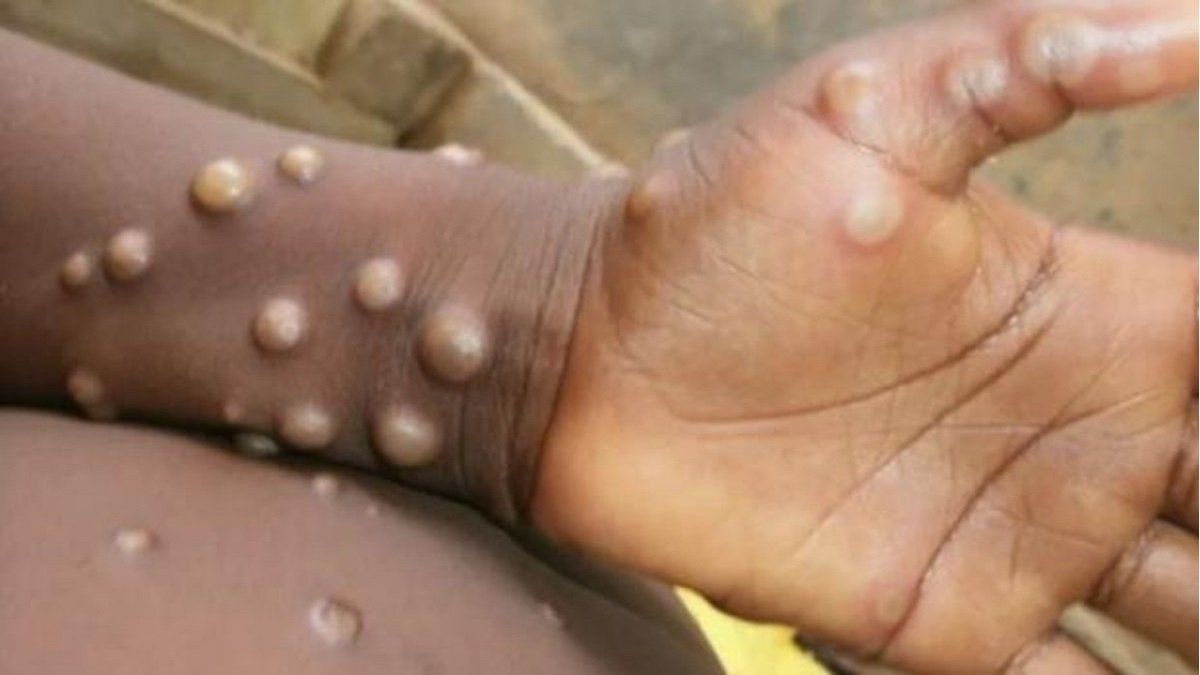
The disease, less dangerous than smallpox, which has been eradicated for about 40 years, is endemic in 11 countries in West and Central Africa. It usually results in a high fever and rapidly progresses to a crusty rash, and infection in early cases is due to direct contact with blood, body fluids, skin lesions, or mucous membranes of infected animals.
Source: Ambito
David William is a talented author who has made a name for himself in the world of writing. He is a professional author who writes on a wide range of topics, from general interest to opinion news. David is currently working as a writer at 24 hours worlds where he brings his unique perspective and in-depth research to his articles, making them both informative and engaging.