The Presidential campaign has put on the table a crucial issue for Argentina: the arrival of new financial technologies such as Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDC). The incorporation of this issue into the political debate underlines the urgency of addressing the implications that the digital world It already has in our daily lives.
In particular, it highlights the need to implement a digital currency that allows us to be technologically up to date with the rest of the world, ensuring greater innovation, greater financial inclusion, instant payments and a more competitive financial system that empowers citizens.
However, still There are serious doubts about what CBDCs arehow they work, what types of digital currencies there are and above all, which countries already have their token in place, as well as which ones have so far raised the debate, such as in Argentina.
Thus, a research team led by Ignacio E. Carballoeconomist, Head of Alternative Finance at PCMI (USA) and Director of the Center for Alternative Finance at the Universidad Católica Argentina (UCA), developed an explanatory document in which this issue is addressed point by point.
What is a central bank digital currency (CBDC)
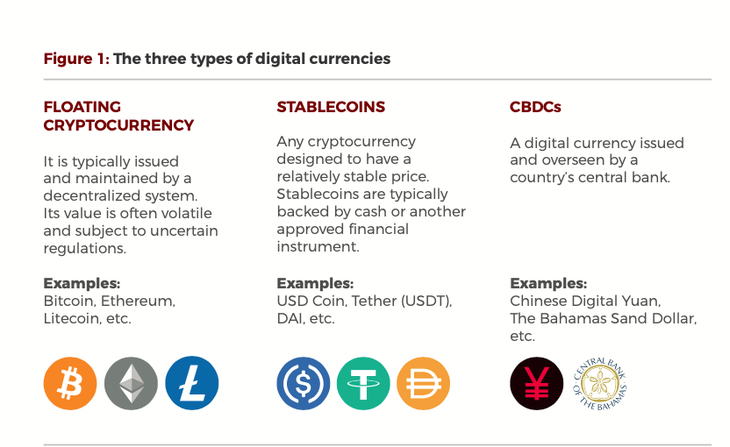
A central bank digital currency (CBDC) is a digital form of money issued by a central bank. Its value is linked to the official currency of the issuing country and legally supported by its regulators. This distinguishes them from other types of cryptocurrencies, like floats or stablecoinswhich are decentralized or maintained by the private sector.
Main characteristics and types of CBDC
- Type of currency: CBDCs can be of two types:
- General Purpose Central Bank Digital Currency: This type of CBDC is designed to be used by the general public, as an alternative to cash or bank deposits.
- Wholesale central bank digital currency: This type of CBDC is designed to be used by banks and other financial institutions, as a means of payment or settlement.
- Technology: CBDCs can be issued using a variety of technologies, such as blockchain, existing payments infrastructure, or an entirely new system.
- Access: Access to CBDCs can be limited or universal.
- Restriction: The use of CBDCs may be restricted to certain purposes or activities.
Current status of CBDCs
As of October 2023, 131 countries, representing 98% of global GDP, are exploring a CBDC. Of these, 64 countries are in an advanced exploration phase (development, pilot or launch).
Screenshot 2023-10-31 at 08.11.41.png
The state of #CBDCs and their implications for the global payments industry
Advantages and disadvantages of CBDCs
Advantages:
- Greater financial inclusion: CBDCs can help increase financial inclusion, providing a secure and affordable means of payment to people who currently do not have access to traditional financial services.
- Improved payment efficiency: CBDCs can help improve payment efficiency, reducing the time and costs associated with transactions.
- Greater security: CBDCs can be more secure than cash, as they are more difficult to counterfeit or steal.
Disadvantages:
- Cost: The development and implementation of a CBDC can be expensive.
- Privacy: CBDCs may raise privacy concerns as transaction records may be public.
- Acceptance: The public may not accept CBDCs as a means of payment.
Screenshot 2023-10-31 at 08.09.45.png
Conclusions
CBDCs are a new technology that has the potential to transform the financial system. However, there is still a lot of work to do to determine if CBDCs are viable and whether they offer net benefits to society.
About the Argentine Digital Currency
In this regard, Carballo maintains in dialogue with Ambit that, an Argentine digital currency would not correct the macroeconomic problems that the national economy presents. “The reality is that a CBDC does not have a direct impact on inflation management on its own.”
Carballo explains that its effect will depend on its configuration and characteristics. “It is similar to a virtual wallet, where the crucial thing is how it is designed and what functions it offers.”. This applies both domestically and internationally, and whether you focus on high or low value transactions. Furthermore, “its relationship with financial institutions and its direct connection with the central bank are important factors.” Also, the ability to implement different monetary policies, such as issuance rate programming and negative interest rates, is relevant, the expert maintains.
For Carballo, the impact of a CBDC in the Argentine context depends on your specific planwhich currently lacks information, making its evaluation and prediction difficult.
For its part, Laureano Bielsa, founder of Criptoperonismo and candidate for national deputy, considers the modernization of the monetary system positive through a digital currency due to the problems inherent to the physical ticket, such as logistics and printing costs and environmental impact.
And points. “The digital currency also “could contribute to reducing informality and tax evasion by making the economy more transparent”. However, he acknowledges that implementing a digital currency poses challenges, especially when it comes to transparency. The crypto expert emphasizes the importance of any step towards a digital currency “be transparent and based on public variables that are not easy to modify.”
Finally, he mentions that the presentation of a formal project in this regard at the Argentine level is still expected, very much in line with Carballo’s statements to this medium.
Source: Ambito
I am a 24-year-old writer and journalist who has been working in the news industry for the past two years. I write primarily about market news, so if you’re looking for insights into what’s going on in the stock market or economic indicators, you’ve come to the right place. I also dabble in writing articles on lifestyle trends and pop culture news.




