According to the latest report, regional economies were affected by lower consumption and high production costs, amid the opening of imports.
He price of agri-food In the month of December it multiplied by 3.9 times from the field to the gondola. That is, the consumer paid $3.9 for every $1 the producer received. On average, the producer’s participation explained 21% of the final sales prices, 11.4% less compared to the previous month. The greatest participation was had by the producers of chicken (54.6%), while the lowest was for those of carrot (9.8%), expressed the latest report from the Argentine Confederation of Medium Enterprises (CAME).
The content you want to access is exclusive to subscribers.
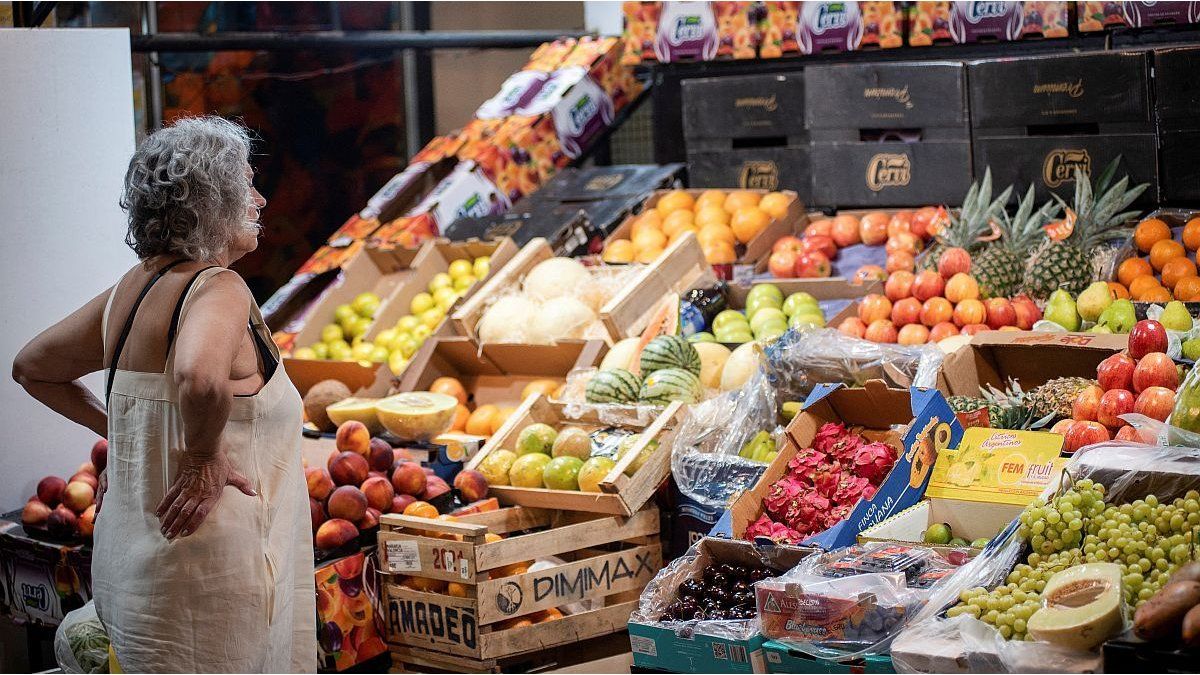
During December 2024, the Regional economies have faced a difficult situation, characterized by weak consumption and high production costs that directly affect local producers. The opening of imports intensified competition, leaving national producers at a disadvantage due to the high costs of inputs, logistics and taxes that make local supply more expensive. In the Central Market of Buenos Aires (MCBA), the entry of table grapes, cherries, oranges, lemons and onions, to mention some products from different origins, was observed in its different warehouses.


unnamed (2).png
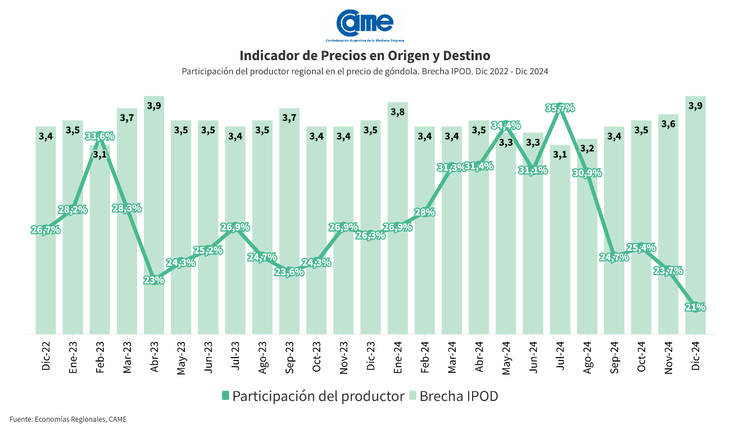
During December 2024, regional economies have faced a difficult situation, characterized by weak consumption and high production costs
The gap in fruit and vegetable products and those of animal origin
Fruit and vegetable IPOD: From the field to the shelf, the prices of the 19 fruits and vegetables that make up the IPOD basket multiplied by 6.9 times in December, which represents an increase of 19% compared to November.
IPOD of animal origin: For the five products and by-products of animal origin that make up the IPOD basket, the consumer paid 2.9 times more than what the producer received. There were no variations with respect to the previous month.
Biggest and smallest IPOD gaps for December
The carrot (10.2 times), the orange (9.6 times), the round tomato (8.8 times), the broccoli (8.8 times) and the cabbage (8.2 times), were the five products that presented the greatest differences between origin and destination prices.
The carrot It decreased 43% at origin and 6.9% at destination, experiencing a sharp drop in prices at origin due to a lack of demand and an excess in supply.
For its part, the price of orange It decreased for the producer (18.9%), and increased for the consumer (1.7%). The decrease in prices at origin was due to the arrival of oranges from Spain and Egypt, favored by the opening of imports. This places the local producer in an unfavorable position, since high production costs considerably increase the price of their supply in the market.
The round tomatoes showed a decrease both at origin (60.1%) and at destination (27.5%). The drop in the price at origin is the result of excess production, which has caused an increase in the supply available on the market.
Lastly, the broccoli and the cabbage presented decreases at origin (22.3% and 50.8%, respectively), since both had a recovery in production levels, while at destination the first increased (19.5%) and the second decreased (14. 8%).
Source: Ambito
I am a 24-year-old writer and journalist who has been working in the news industry for the past two years. I write primarily about market news, so if you’re looking for insights into what’s going on in the stock market or economic indicators, you’ve come to the right place. I also dabble in writing articles on lifestyle trends and pop culture news.




