Every September 7th the World Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Awareness DayThis year, the theme is “Speak up for Duchenne” in order to create a society that provides equal opportunities for all.
This year’s theme emphasizes the importance of amplifying voices to advocate for the rights, inclusion and well-being of people living with Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD).
For this reason, society, regardless of their personal connection to Duchenne, is invited to join together to create a more inclusive world where people living with disabilities are empowered to thrive.
What is Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy?
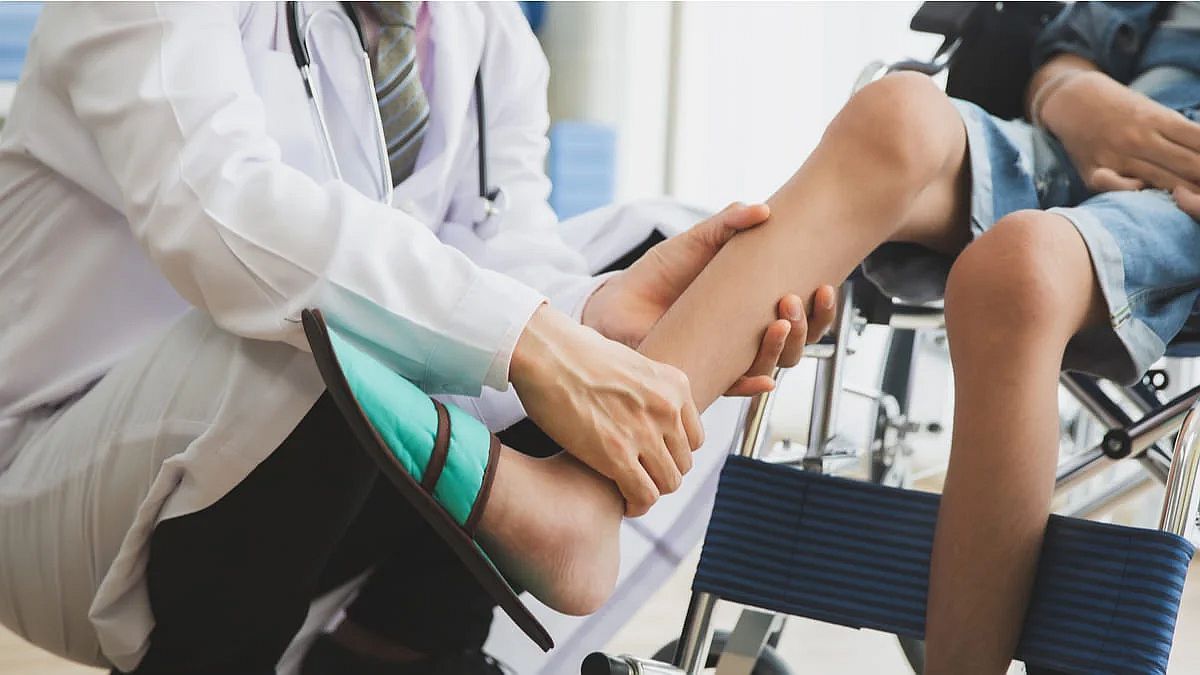
People with Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) face physical, health and social barriers. This severely limits their ability to participate fully in community life and activities.
The goal of raising awareness and visibility is to break down barriers to promote inclusive education that provides opportunities for people with DMD to have a bearable daily life with optimal care.
What causes Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy?
DMD is a rare genetic disease that causes progressive muscle weakness. It is caused by a mutation in the gene that encodes dystrophin, a protein crucial for muscle function.
A portion of the DNA is missing, duplicated, or changed so that the code cannot be read correctly and protein production fails. Without dystrophin, muscles weaken and deteriorate progressively, leading to loss of strength and mobility.
The dystrophin gene is located on the X chromosome, which generates a particular inheritance pattern: women (XX) behave as carriers (they may present mild symptoms and heart disease) and men (XY), having a single copy of the gene, will have earlier and more symptomatic clinical presentations. In some cases the mutation can occur spontaneously.
According to statistical information provided by the World Duchenne Organization (WDO), every year, 1 in 5,000 boys are born with DMD worldwide and the average age of diagnosis of DMD is 4.5 years.
What are the signs to look out for?
- Delay in acquiring walking
- Difficulty walking, running or climbing stairs
- Waving gait
- Frequent falls
- Difficulty getting up from the floor
- Decreased strength
- Delay in speech and language development
Early diagnosis in children enables multidisciplinary treatments and care that improve quality of life and provides families with the information necessary for thoughtful family planning.
What to do in case of early detection of the disease?
Getting the right care and talking to your doctor about available services and support is one of the most important steps you can take as a Duchenne patient.
Early care will give your family the best chance of coping with Duchenne muscular dystrophy. In addition, an early diagnosis of your child’s symptoms is critical to speeding up the process. The sooner a diagnosis is made, the sooner treatment can begin and planning can begin accordingly. This means you and your child or loved one can:
- Be referred to specialist teams close to your home
- Start treatment as soon as possible
- Gaining access to genetic counseling
- Allow family members to undergo genetic testing
- Plan ahead and anticipate potential changes related to your employment and housing
- Making decisions about family planning
- Receive assistance from local patient organizations and the patient community.
How is Duchenne muscular dystrophy treated?
Duchenne muscular dystrophy causes muscle weakness that progresses over time. This means that walking, standing and performing everyday tasks become increasingly difficult.
While the progression and severity of symptoms differs for each child, most will experience some of the stages shown below in the infographic.
image.png
Receive a diagnosis of Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) It can be a difficult time, but to get through this situation, it is vital to have the care team as they offer information and assistance as you need it, so reaching out to them can be a great decision.
The team is made up of health professionals such as pediatric neurology a specialist in conditions of the brain, spinal cord, and nerves. This professional usually leads and coordinates the Duchenne care team; kinesiologyworks to improve muscle and joint function; occupational therapy to develop skills to perform everyday activities; traumatologyto treat bone and joint disorders; cardiology since DMD patients need regular check-ups to detect heart muscle disorders, which are also affected by the absence of dystrophy; pulmonologyto monitor the functioning of the respiratory system. The equipment is completed with Clinical Nursing Specialist to provide care; gastroenterologytogether with nutritionist They manage aspects of diet, gastrointestinal mobility, weight, reflux and swallowing disorders. Social work, psychology or psychiatry to support patients and families to provide containment regarding services. GeneticistThis health professional specializes in medical genetics and provides support in family planning and study.
image.png

Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy: the iResearch and development
A better understanding of DMD encourages support for scientific research. This is vital for the development of new therapies that can offer better results in managing the disease, and even find a cure.
This day is an opportunity to join forces globally, share valuable information and support those living with DMD, their families and the researchers who work tirelessly to find solutions.
Source: Ambito
I am Pierce Boyd, a driven and ambitious professional working in the news industry. I have been writing for 24 Hours Worlds for over five years, specializing in sports section coverage. During my tenure at the publication, I have built an impressive portfolio of articles that has earned me a reputation as an experienced journalist and content creator.