The tomanufacturing activity of SMEs It fell 6.6% year-on-year in September and accumulates a decline of 15.1% in the first nine months of the year compared to the same period in 2023. It is the lowest rate of decline in 10 months and in the seasonally adjusted month-on-month comparison there is an increase of 3.7%. according to the Argentine Confederation of Medium Enterprises (CAME).
Meanwhile, of the 6 sectors surveyed, 5 of them improved their activity in the seasonally adjusted inter-monthly comparison. For his part, the Use of installed capacity continues to be very low. It is 60.6%, a consequence of an activity that remains depressed, especially in textiles and clothing, where it stood at just 54.6%. That is precisely one of the main areas with problems paying salaries, according to 24.1% of the responses.
unnamed.png
The use of installed capacity continues to be very low, at 60%
SME industry: how each sector fared in September
The six manufacturing sectors of the SME segment had sharp falls in the annual comparison, The most affected being “Paper and Printing” (-20.7%) and “Food and Beverages” (-8.3%). “Wood and furniture” It was the branch that contracted the least (-0.6% annually).
The sector recorded an annual decline of 8.3% at constant prices in September and an improvement of 1.9% in the monthly comparison. For the first nine months of the year, there is an annual decrease of 15.5%. The industries operated with 62.2% of their installed capacity.
2. Textiles and clothing
Production fell 7.3% annually and -0.8% compared to August. In the section of the first nine months of 2024, there is a contraction of 4.6%. The factories worked with 54.6% of their installed capacity, being the category with the least use of their facilities in the month.
3.Wood and furniture
In September, the sector fell 0.6%, always annual and at constant prices, and grew 2.8% in the seasonally adjusted monthly comparison. In the January-September period, activity decreased 13.3% compared to the same months last year.
4.Metal, machinery and equipment, and transportation material
There was a decrease of 2.6% in September, and it grew 5.4% in the monthly comparison. In the first nine months of the year, there was a 16% drop, always compared to the same period in 2023. The industries operated at 60.1% of their installed capacity.
5.Chemicals and plastics
The sector experienced a contraction of 8%, and a rebound of 5.3% in the monthly contrast. Until September, a decline of 21% is recorded, compared to 2023. During this month, industries occupied 63.7% of their installed capacity.
6. Paper and prints
Activity fell 20.7% annually at constant prices, being the sector with the greatest decline. In monthly terms, however, it had an increase of 9.1%, becoming the sector with the greatest recovery compared to August. For the first nine months of the year, activity accumulated a drop of 16.8% compared to the same months last year. The companies operated with 59.4% of their installed capacity.
unnamed (2).png
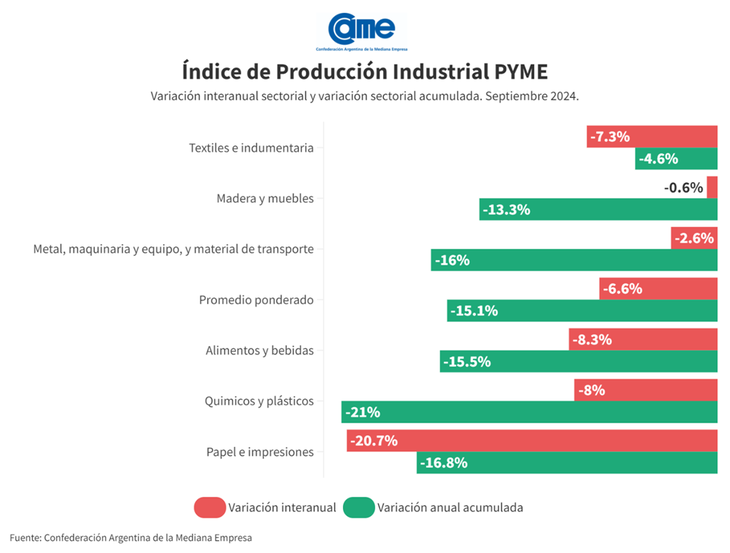
The six manufacturing sectors of the SME segment had sharp falls in the annual comparison, but an improvement in the monthly analysis.
The opinion of companies, according to CAME
The most notable measure that SME industries expect is the tax reduction (national and provincial) and municipal taxes. This joint demand represents 59.8% of the responses, followed by the stimulation of domestic demand with 13.9%.
Companies are more concerned about high costs outside the production process than about the drop in production itself, where they somehow expect a speedy recovery.
The generation of incentives for the hiring of personnel It ranks fourth among the decisions considered most effective for SMEs in the short term, with 8% of the responses. In any case, that percentage was decreasing in recent months due to the lower intention to hire personnel in the face of the drop in activity.
In addition, In September the obstacles identified by businessmen are the lack of sales, which represents 41.3% of the responses and continues in first place, along with high production and logistics costs, which constitute 36.5%. These two factors stand out as the most significant difficulties for the growth and stability of SMEs.
Faced with a context of low demand and high fixed costs32.6% of the companies consulted were reducing expenses operational. Meanwhile, another 30.4% diversified their manufacturing, incorporating new products and providing additional services to their usual activity. In turn, 11% of industries reduced working hours.
With respect to the distribution of SME industrial companies that experienced difficulties paying salaries, During September, broken down by category, it is observed that the “Textile and clothing” sector leads with 24.1% of companies reporting problems. Behind it is “Metal, machinery and equipment, and transport material” with 22.4%. Other branches affected include “Food and beverages” (17.2%) and “Chemicals and plastics” (15.5%). For their part, the categories “Wood and furniture” and “Paper and printing” presented the lowest proportion of companies with problems, both with 10.3%. It is observed that the pressures are mainly concentrated in labor-intensive sectors with high exposure to volatile variable costs.
Source: Ambito
I am Pierce Boyd, a driven and ambitious professional working in the news industry. I have been writing for 24 Hours Worlds for over five years, specializing in sports section coverage. During my tenure at the publication, I have built an impressive portfolio of articles that has earned me a reputation as an experienced journalist and content creator.




