Argentinians surveyed maintain the expectation that inflation will continue to decline in the long term. For what is this?
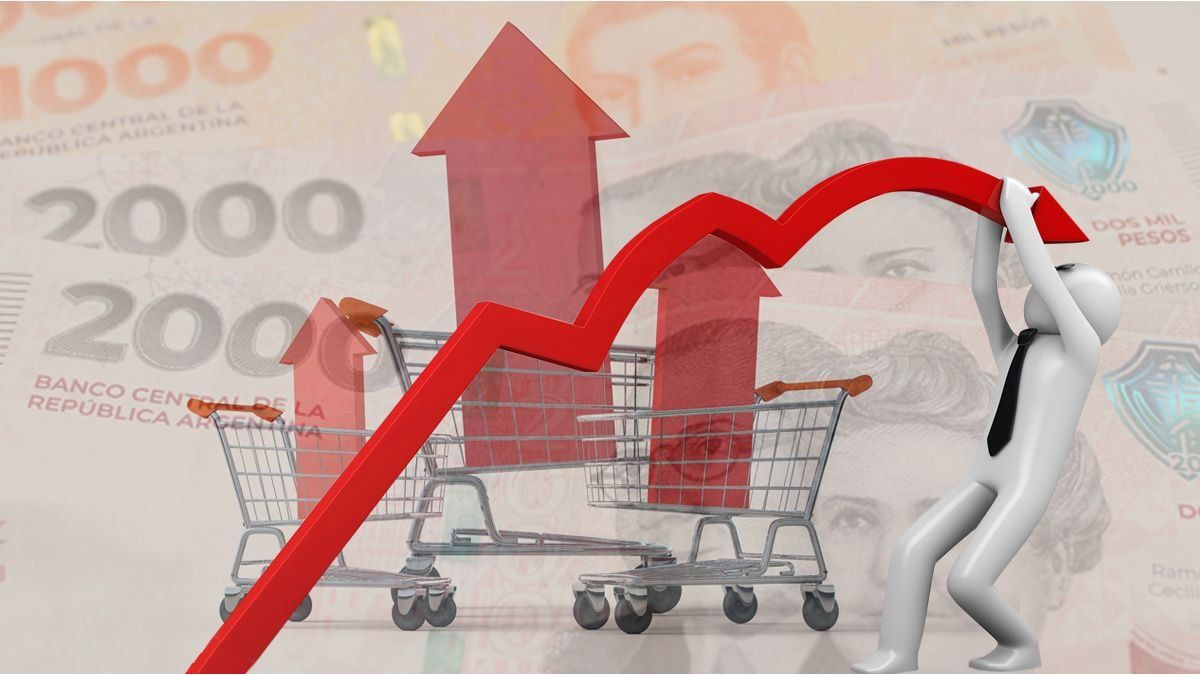
There is a strong inflation reduction expected by the population for the next 12 months, according to a report prepared by the Di Tella University. In the February measurement it was 170.8%, and in the March measurement (carried out between March 4 and 13) it is 123.8%, according to the average (100% according to the median).
The content you want to access is exclusive to subscribers.
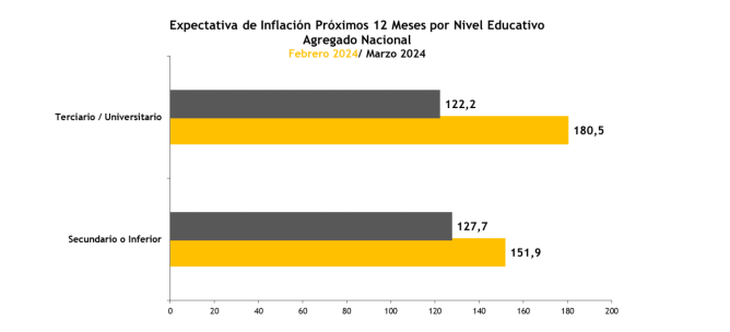
By region, the interior of the country returns to show the lowest annual inflation expectations, 111.2%, compared to 148.2% and 140.7% for CABA and GBA respectively. Compared to the February measurement, the reduction in expected inflation was general, by region and by different income levels. An interesting aspect is that the Inflation expectations are very similar by income level, 122.2 and 127.7 for those at high and low levels, respectively, since very different perceptions were observed between both groups.


Refering to expected inflation for the next 30 days, It also fell, currently being 15.46%, when in February it was 19.08% (the median also decreased from 20% to 15%).
“We found that people have less dispersion of opinion in monthly inflation than in annual inflation. In March 2024, the Inter-quartile range of monthly inflation was between 20% and 10%, with a median of 15%, less than that of February (20%)”, they expressed from Di Tella.
Expected inflation decreases in all regions of the country
The sampling is representative for three regions: the City of Buenos Aires (Capital), the Buenos Aires suburbs (GBA), and the rest of the country (Interior). This month, Di Tella observed that Expected inflation values decrease considerably in CABA and GBA compared to those registered last February.
The expected inflation for the next 12 months in GBA is 140.7%, 61.1 pp lower than the February measurement, 201.8%. In CABA it is 148.2%, 66.3 pp lower than the 214.5% reported in February.
The average expected inflation perceived by households falls for everyone beyond the income level
During the month of March we observed a significant reduction in expected inflation among households of different educational levels (which also approximates the level of income), and a change in trend. Unlike recent months, the values reported this month show that individuals with a higher educational level have lower inflation expectations. Individuals with a lower educational level registered a decrease in perception, going from 151.9% in February to 127.7% this month, while those with a higher educational level went from a value of 180.5% in February to 122. .2% in March.
level4.PNG
Source: Ambito




