The process of elimination of exchange controls “will be defined by the Argentine authorities themselves, contemplating the evolution of the relevant economic variables, who will share with the IMF the parameters that will be monitored, without including commitments of specific dates or measures,” specifies a statement released this Thursday by the Ministry of Economy and the Central Bank referring to the approval of the eighth review of the agreement that the country has with the multilateral organization. In this way, the authorities ratify “flexible” management of monetary policy.
Official information confirms that The Central Bank “considers advancing in the liberation of exchange controls and greater exchange flexibility,” but he warns that he will “as long as these measures do not imply excessive risks for the process of reducing inflation and strengthening its balance sheet.”as reflected in the agreement with the Fund.
The authorities specified that, after the approval of the latest review of the Extended Facilities Program in force with Argentina, the disbursement of around US$790 million is released. an amount that exceeds the next amortization to the IMF (July 2024) of approximately US$645 million. It also clarifies that the payment scheduled for July is the last amortization payment to the Fund contemplated within the framework of the current program that expires in November 2024. As of that payment and for the next 2 years (until September 2026), Argentina does not face any more principal repayment maturities with the multilateral organization.
IMF Chart.png
IMF Chart (2).png
IMF Chart (3).png
Bookings
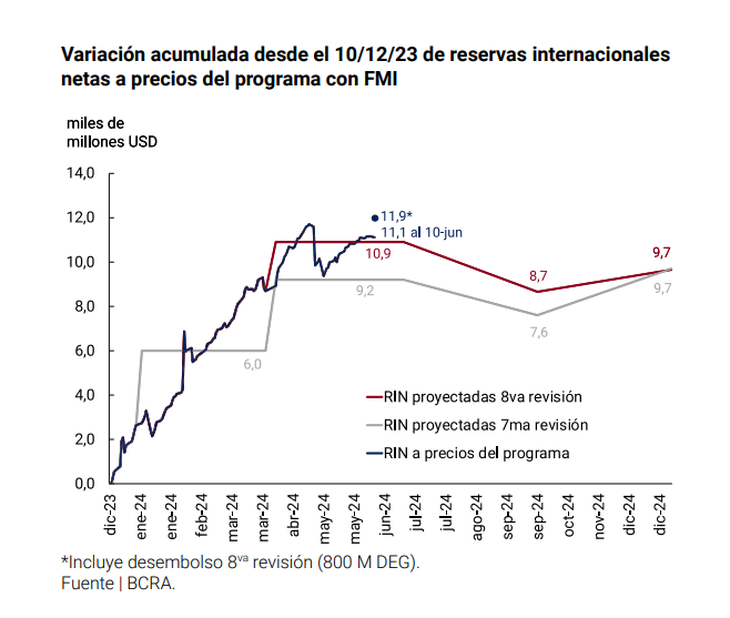
The statement states that The Central Bank accumulated US$ 9 billion of Net International Reserves (RIN) as of March 31, the goal as of that date being US$6 billion. Specifies that “this baggy overfulfillmentadded to the growth of the RIN observed in the following months, shows a cumulative recovery of US$11.3 billion as of today, which will soon be increased by the approved disbursement of US$790 million.
Given that the current level of reserve accumulation already exceeds that foreseen in the program for the entire second quarter (original goal of US$9.2 billion as of June 30, 2024), it was agreed to raise the second quarter goal to USD10.9 billion, without affecting the original annual goal (which remains at $9.7 billion as of December 31, 2024).
Fiscal Balance
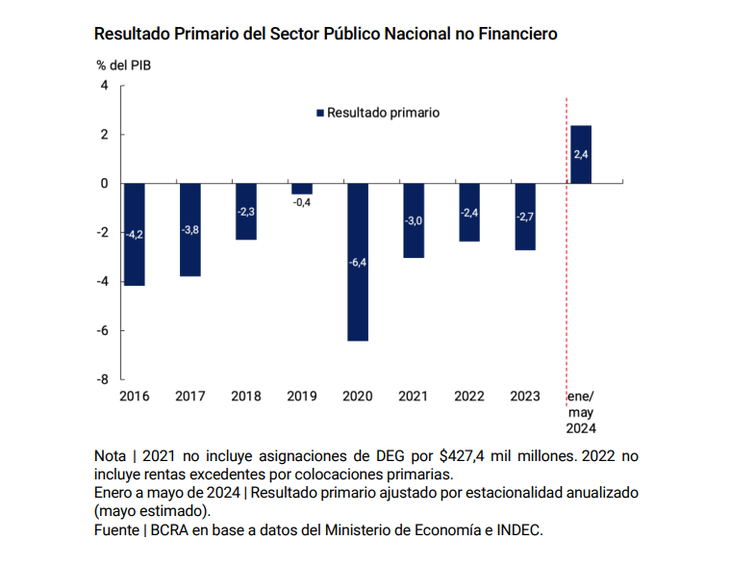
“The objective of financial balance contemplated in the Agreement was achieved in record time“, says the statement. It points out that starting from a financial deficit of 4.6% of GDP in 2023, in the first quarter of the year The primary surplus amounted to 0.7% of GDP and the financial surplus to 0.2% of GDP. This result “It was achieved with a combination of permanent spending cuts and temporary tax increases”.
The authorities maintain that “fiscal balance was achieved without neglecting the most vulnerable populationsignificantly reinforcing social programs that, without intermediaries, reach the beneficiaries directly.”
In particular, it stands out that the Universal Child Allowance increased 335% between November 2023 and June 2024, resulting in an estimated increase in real terms of 90%. The Alimentar Card and the First Thousand Days of Life program also showed real increases estimated at 4% and 470% in said period. Retirements without including the bonus registered an estimated increase of 3% in real terms, as a consequence of the 12.5% reinforcement granted in April and the change to an automatic update for inflation with a two-month delay enabled by the Necessity Decree and Urgency 274/2024 of the National Executive Branch. Anticipate that “it is to be expected that retirements will continue to grow in real terms given the ongoing disinflation process.”
For the second semester, he anticipates that “with the economy returning to growth and the full effect on the fiscal accounts of the changes in energy rates, the update in the fuel tax and the reduction in operating expenses, the Government expects to initiate a significant reduction in “more distortive taxes, starting with the PAIS Tax once the Bases Law is enacted”.
Monetary contraction
The document indicates that while in the 12 months prior to the change of government the BCRA had financed, directly and indirectly, the Treasury by $50 billion (at June 2024 prices), these flows were reversed as of the new administration.
He states that at the end of the first quarter The BCRA’s net monetary financing to the Treasury showed a current balance of -$2.1 trillion, exceeding the quarterly goal that contemplated a limit of $0.
He emphasizes that “this balance represents a source of contraction in the amount of pesos in circulation, thus contributing to the cleanup of the BCRA’s balance sheet.” However, he clarifies that it does not reflect the full monetary impact of Treasury operations. At the moment “the goal of net monetary financing to the Treasury continues in negative territory (-$82 billion current) and the contractionary monetary impact of the Treasury’s operations results in a much higher total absorption of pesos by the BCRA, $17 billion, contributing to the disinflationary process”.
He also points out that the BCRA chose to prioritize actions with the objective of “drastically reduce endogenous monetization” originated from the interest on remunerated liabilities. Interest on these liabilities fell by 80%, from more than $5 trillion in November 2023 (at current prices) to around $0.6 trillion per month today, “contributing to anchoring inflation expectations”.
Thus, he states that “Along with the strong progress in solving the debt of importers The surplus of the broad monetary base (monetary base plus remunerated liabilities) has been reduced, approaching today levels of the monetary base that have historically been associated with periods of equilibrium in the money market. He adds that the macroeconomic balance resulting from the over-fulfillment of the three goals established in the Agreement with the IMF together with the other actions of the authorities has contributed to a rapid reduction in inflation.
Exchange rate policy
Finally, the statement considers “of importance highlight two objectives of the Argentine economic authorities reflected in the Agreement that are ratified in the eighth program review with the IMF: the timely presentation of a monetary programming framework and the elimination, without conditioning of times or forms, of exchange controls.”
The authorities point out that “The BCRA will continue to conduct monetary policy in a flexible, prudent and pragmatic manner”. Anticipates that, based on the progress achieved in the recovery of monetary policy tools and the control of money creation factors, The Agreement provides for the presentation to the IMF of a monetary programming framework at the end of June 2024..
The statement states that “The purpose of this framework is contribute to further reducing uncertainty by providing more information on the projected behavior of monetary variables consistent with the continuity of the macroeconomic stabilization process.”
Source: Ambito




