For next year, the Government expects the economy to grow 5%, inflation to slow to 18.3%, the official dollar to advance at a pace similar to prices, reaching $1,207 in December, a primary surplus of 1.3% of GDP and a balance in the financial results of the Treasury.These are the main macroeconomic data contained in the budget project that the Executive Branch submitted to Congress.
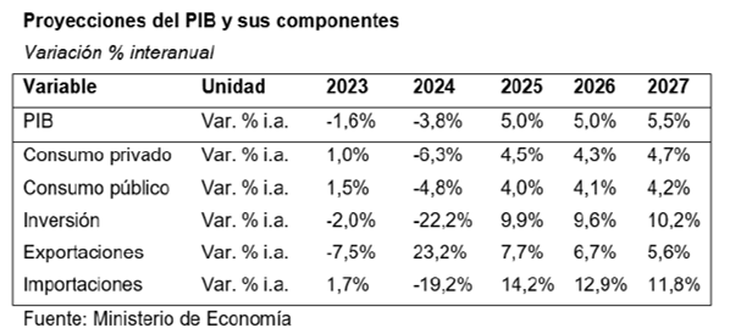
The Ministry of Economy estimates contemplate a 3.8% drop in gross domestic product for the current year, but a significant recovery of 5% by 2025This percentage is above the private projections contained in the Market Expectations Survey (REM) which expects an average growth of 3.5% for next year.
The Government projects that “continue sustained GDP growth in the following years,” According to the budget message, with expansion rates of 5% in 2026 and 5.5% in 2027.
Authorities anticipate a marked slowdown in inflation, which could reach 18.3% next year, far from the 104.5% increase in the consumer price index during the current yearo. This implies an average inflation of 1.4% per month.
image.png
The official forecast is located below REM estimates which anticipate a price index increase of 38.4% by 2025.
However, the message clarifies that given the formal steps involved in the budget process, the macroeconomic scenario used as input was prepared in June.
Since then, the data that has been published allow us to project, for 2024, a smaller drop in GDP than estimated, also associated with inflation somewhat higher than expected at the start of the preparation of the Budget.
How much will the dollar be worth in 2025, according to the Budget?
A key fact:The authorities are considering a progressive adjustment of the official exchange rate. The Government’s calculations assume that the official dollar is located in December of this year at $1,019.90 and an increase of 18.3% by 2025, which would take the official dollar to $1,207 in December 2025.
In this way, the Government insists on maintaining its exchange rate policy, ignoring the arguments of those who point out, such as the IMF, that the exchange rate is outdated.
GDP growth in 2025, according to the Budget
For 2025, official forecasts anticipate that growth of GDP is driven mainly by industry and commerce, with increases of 6.2% and 6.7%, respectively..
For its part, it is expected that the agricultural sector advances 3.5%In sum, goods items grew by an average of 5.6%, above services, which rose by 4.4%.
image.png
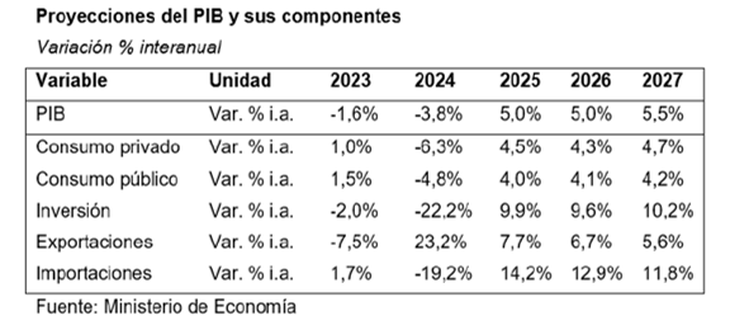
On the demand side, a recovery is expected in all components; in particular, Private Consumption grows 4.5% and Investment, 9.9%.
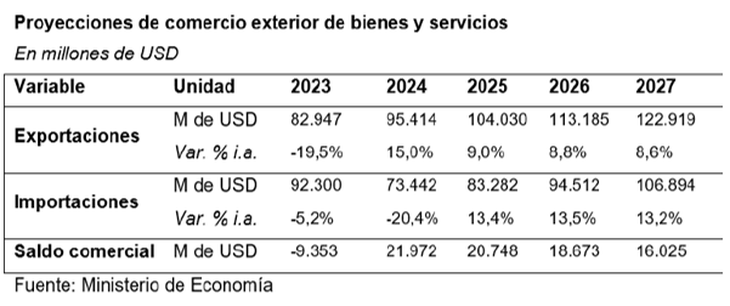
The Government expects a surplus of US$20.748 million for next yearresulting from an increase in the exported value of goods and services by 9.0% and an increase of 13.4% in imports.
image.png
Budget 2025: surplus
The 2025 budget project includes a financial surplus of $190.655 millionslightly in surplus in terms of GDP, while The primary result would reach $1,473,426 million, that is, a surplus of 1.3% of GDP.
image.png
The message highlights that Since 2014, a balanced budget has not been presented to the National Congress. Furthermore, he argues that Since 2010, there has not been an annual fiscal surplus, and since 2008, there have not been two consecutive years of financial surplus..
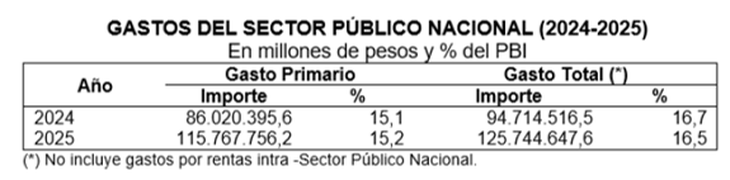
The total estimated resources for the 2025 fiscal year amounts to $125.9 billion, equivalent to 16.5% of GDPwith a drop of 0.2 points compared to 2024.
image.png
For its part, the total consolidated expenses of the National Public Sector reach $125.7 billion (16.5% of GDP), While, after discounting the net interest expense on public debt, primary expenditure represents 15.2% of GDP.
Total expenditure is lower than that estimated for 2024 (-0.2 percentage points of GDP), while primary expenditure is higher by 0.1 percentage points of GDP.
2025 Budget Priorities
The draft budget message also presents the 10 main budget programs, which “reflect the change in priority in those policies related to the axes of this administration.”
Firstly, there is an increase in the ranking of programmes associated with social assistance without intermediaries, such as family allowances and food policies.
For its part, The educational policy associated with higher education also grows in hierarchy compared to 2024 and 2023.
In the opposite direction, There is a clear drop in the hierarchy of energy policy, which is due to the decision to focus and make the allocation of energy subsidies more efficient, both in 2024 (-40% real year-on-year as of July) and in 2025, which in turn reflects the objective of reduce the level of intervention of the National State in the market.
Finally, The drop in the ranking of land infrastructure expenditure stands out, related to the drop in capital expenditure and the discontinuity of minor works.
image.png
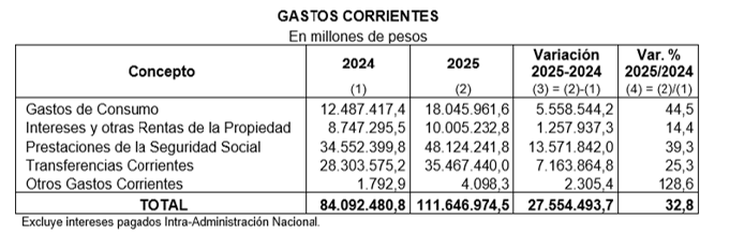
image.png
Source: Ambito




