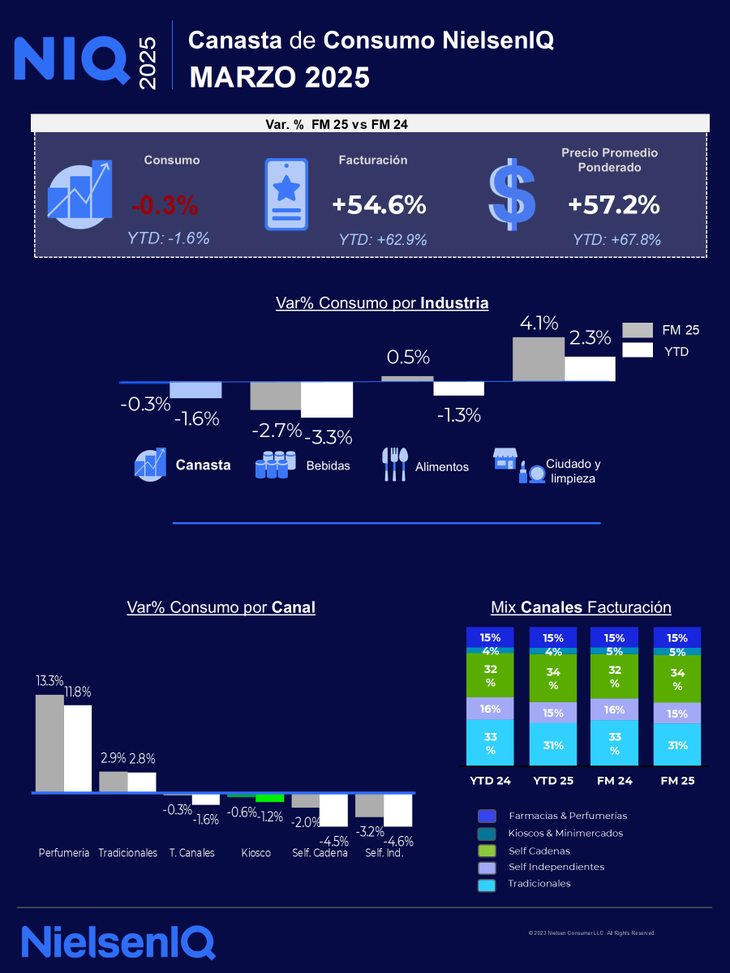
In the month of March, the billing fell to 54.6% (vs 70.9% February), marking the impact of consumption price rise, according to a private report.
Mass consumption contracted again in March, with an interannual fall of the 5.4%according to a private report. The decline deepens the recoil registered in February, when the contraction had been of the 2.7%in a context marked by the loss of purchasing power and the persistent impact of inflation on essential products.
The content you want to access is exclusive to subscribers.
Something to highlight is that in March, billing fell to 54.6% (vs 70.9% February), marking the impact of consumption price rise. Nielseniq’s report also explained that the consumption of basic foods a one fell 4.5% In March. In contrast, the Non -basic foods registered a slight growth of 1.9%like candieswith an advance of 2.2%.


Together, the item food achieved a moderate increase in 0.5%but driven by non -essential items. Within the categories surveyed, the sector drinks It was the only channel that showed a net contraction. The alcoholic beverages They were the most affected, with a fall in the 10%while Without alcohol They showed a marginal rise in 0.5% compared to previous months.
Outside food, the category of Personal care and cleaning exhibited an average growth of 4.1%disaggregated in an increase in 3.8% in cosmetics and dressing table and of 4.9% in home and clothing cleaning.
Image003.png
The impact of consumption inflation
The fall in consumption occurs in a strong price increase context. In March, inflation reached 3.7%mainly driven by the items of Education (21.6%) and food (5.9%)according to INDEC data.
He Consumer Price Index accumulates a rise of 8.6% in the year and an increase in 55.9% year -on -year. The price rise in vegetables, tubers, legumes, meats and derivatives It had a high incidence in all regions.
Source: Ambito




