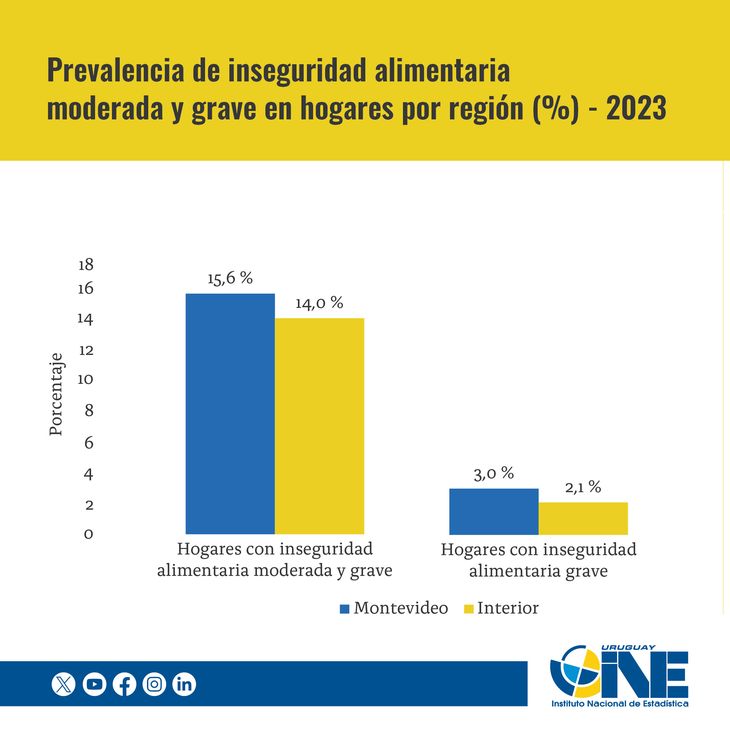
The data is similar to last year, with a higher prevalence in the northeast region, as well as in Montevideo and Canelones.
14.6% of Uruguayan homes suffer from moderate or severe food insecurity, according to a report by the National Institute of Statistics (INE), who attributed this situation to the reduction in the amount of food, either due to lack of money or other resources.
The content you want to access is exclusive to subscribers.
The figure grows to 16.3% if the estimate of food insecurity, remaining a prevalent problem in the country, even in homes where there are children. From the survey it is clear that the areas with the greatest difficulties are the northwest region, Montevideo and Canelones.


Specifically, the text estimated the prevalence of food insecurity severe in households was estimated at 2.5%, which means that they were left without food due to lack of money or other resources and that someone in the house did not eat all day.
Meanwhile, by geographical area, the INE recorded a higher prevalence of food insecurity in the northeast region, made up of Artigas, Tacuarembó, Rivera, Cerro Largo and Treinta y Tres, as well as in Montevideo and Canelones, while the lowest levels corresponded to the departments of the center and southeast of the country.
INE food insecurity graphic.jpg
The data according to household income
When measuring the problem by income level, it can be seen that it was mainly concentrated in households in the first quintile, where food insecurity moderate or severe reached 37.1%, with severe reaching 8%.
The percentages decreased markedly as household income increased. For example, in households in quintile 5, the prevalence was 2% and 0.2%, respectively.
Regarding homes with minors, the food insecurity It was higher in those living under 6 years of age, reaching 19.9%, with 3.3% in serious conditions. Meanwhile, in households with children under 18 years of age, the problem was 19.1%, with 3.4% of serious cases.
From the INE They highlighted that “the changes are not statistically significant” with respect to the 2022 report, although they called for continuing with the measurement to design medium and long-term approach strategies.
Source: Ambito




