The government of Brazil arranged increase the military presence in the northern border due to the increase in tensions between Guyana and Venezuela following the historical territorial dispute over the Essequibo region, an area rich in mineral resources. The Bolivarian Republic promotes a referendum to annex the area.
“The Ministry of Defending has been monitoring the situation. The defensive measures have intensified in the northern border region of the country, promoting a greater military presence,” said the Brazilian ministry in a statement released this Wednesday night.
Lula da Silva’s administration reported that “has intensified defensive measures” along its northern border in the face of the territorial dispute.
nicolas mature 2023.jpg
Venezuela promotes a referendum
The governments of Nicolas Maduro drives a referendum consultative for the next December 3 in which it will ask its citizens if they support granting nationality to the 125,000 inhabitants of Essequibothe disputed region, and create a new Venezuelan province called “Guiana Essequiba”.
Guyana rejected the consultation, which was described by its president, Irfaan Ali, as “a threat to peace in Latin America and the Caribbean”.
“I tell the leaders of the Cooperative Republic of Guyana, this is resolved as President Nicolás Maduro has said: with dialogue, with diplomacy, talking, reaching an agreement satisfactory to both parties as stated in the Geneva Agreement” , which Venezuela signed in 1966 with the United Kingdom before Guyanese independence, Irfaan then added.
Guyana raised tension by proposing the installation of military bases
Guyana days ago he raised the option of establish “military bases” with US support in Essequibo, territory rich in oil and natural resourcesfor which he maintains a long controversy with Venezuela, who called the announcement “provocation”.
“We have never been interested in military bases, but we have to protect our national interest,” declared the Vice President of Guyana, Bharrat Jagdeo, at a press conference.
“We are interested in maintaining peace in our country and in our borders, but we have been working with our allies to ensure a plan for all eventualities”, he added and announced the visit of officials from the United States Department of Defense next week.
“We will have the visit of two teams from the United States Department of Defense next week and then several visits in December and a high-level representation,” Jagdeo said.
“All available options will be taken advantage of,” said the vice president, according to the AFP news agency.
image.png
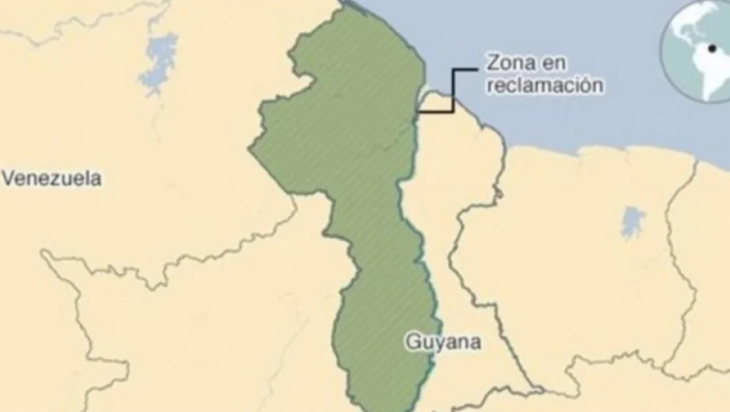
What is Essequibo and what are the riches in the territory?
Essequibo has a larger area than countries like England, Cuba or Greece and is a territory with a high presence of natural resources such as minerals and oil. Since 1841 both countries have disputed their sovereignty.
Venezuela’s claim to the Essequibo territory has a long history. However, since 2015 the Maduro government has raised its voice after vast oil reserves were discovered.
The Bolivarian Republic usually includes Guyana Esequiba as a region “in claim” and its maps reference it but in a crossed out manner.
“I tell the leaders of the Cooperative Republic of Guyanathis is resolved as President Nicolás Maduro has said: with dialogue, with diplomacy, talking, reaching a satisfactory agreement for both parties as stated in the Geneva Agreement“, which Venezuela signed in 1966 with the United Kingdom before Guyanese independence, he then added Irfaan.
That document annulled the arbitration award of 1899, who set the current borders and? Georgetown claims, and established bases for a negotiated solution.
The struggle intensified with the discovery of oil fields in the region and Guyana’s negotiations with the American energy giant ExxonMobil for its exploitation.
Amid an escalation of mutual accusations in recent weeks, the president of Venezuela denounced this Thursday “a dirty campaign” by ExxonMobil against the referendum.
The United States led military exercises in Guyana in July, with the participation of more than 1,500 troops from 20 countries.
Source: Ambito




