Days ago, The Central Bank decided to make the restrictions on access to dollars more flexible And he enabled banks to finance all types of people and companies in foreign currency, despite not having their income linked to the US currency. As he said Scopethe measure aroused rapid warnings of economists about their implications. This Tuesday, the Risk Qualifier Moody’s analyzed the initiative and He pointed out that he could help boost credit, although he warned that financial institutions will be exposed to the possibility of suffering higher levels of default.
Through communication “A” 8202 of February 20, 2025, the BCRA flexible the provisions that limited the granting of credit in foreign currency to companies that would not generate dollars genuinely. It was not a total liberalization: it was established that Foreign currency deposits can only be provided to exporters, as until now, but that banks can grant credit in dollars to the rest of their clients if the currencies obtain them through the placement of negotiable obligations (ON) or other external financing.
The warnings soon arrived since the measure implies to begin to make macroprudential norms that arising from the 2001-2002 crisis experience that, according to many economists, were key to avoiding a bank crisis in the subsequent 23 years.
Dolk loans: Moody’s analysis
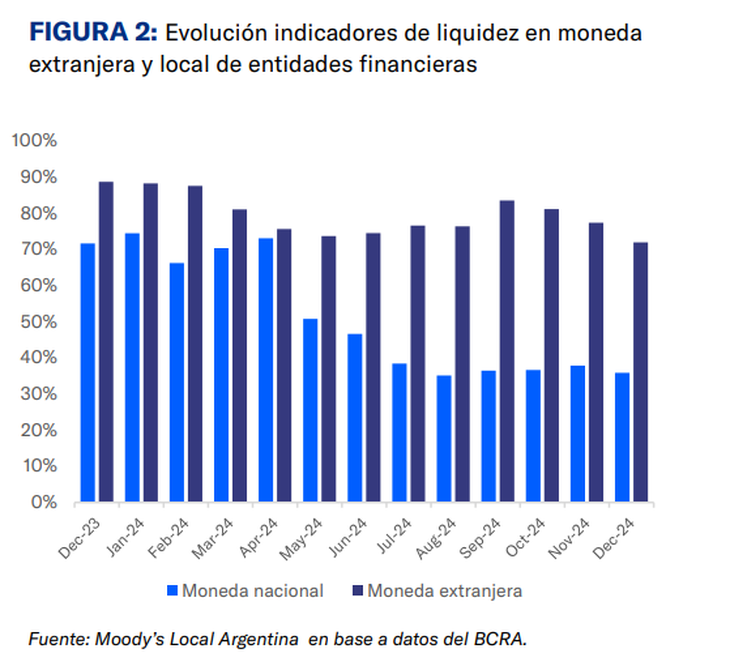
“The new regulations boost the path of expansion of the credit in dollars to the private sector”, Moody’s said in a report published Tuesday. In the last year, the qualifier highlighted, there was a growth of the credit in foreign currency (212% year -on -year in 2024 and 16.8% only in December) motivated by the gradual normalization of the macro and destined for companies with income in dollars. That expansion relied on the increase in deposits in foreign currency that left the money laundering.
image.png
“The regulatory change will allow to cover the unsatisfied demand for foreign currency to companies of non -export sectors or currency generators,” said Moody’s.
The firm considered that it is positive that this regulatory change does not include the possibility that financial entities use deposits in dollars to anchor these credit operations since “shelters the credit profile of the banks and limits the decrease in dollar liquidity.” And he added that, “in this way, the deposits in dollars are protected in front of currency declines and the bank exposure is limited only to their own funds.”
Loans in dollars and default risk
However, Moody’s warned that “The banks of the banks could be pressured by the risk of coin barefoot”that is, because of the fact that the public is given in a currency in which you do not have your income.
“By allowing access to dollars to companies that do not generate currencies The risk of the eventual exchange rate of the exchange rate by the credit takehies breastfeeding their obligations “is increased in the event.”considered.
In any case, he indicated that this risk “is partially mitigated by the expected exchange stability by 2025 and by the low historical levels presented by the banking system today.”
image.png
Other effects of measure
Likewise, the qualifier stressed that the official decision It will cause banks to increase their presence in the capital market through the issuance of ON dollars to fund these loans.
In that sense, he stressed that, from the second semester of 2024, the capital market was positioned as an alternative to obtain anchor for financial intermediation operations effect of improvement in macroeconomic conditions. The volume issued by financial entities grew significantly and exceeded US $ 10,000 million and among the main issuers, Banco Galicia, Banco Supervielle and Banco Comafi stood out.
In that sense, he concluded: “The demand for these instruments was correlated with the liquidity in dollars prevailing in the market after the money laundering. Likewise, the decrease in the ‘Crawling PEG’ rate generated a greater demand for instruments ‘hard dollar’ to the detriment to the ‘dollar Linked’, which generates a propitious context for the issuance of ON for the fund of loans. The banks placed in the market 13 ON and 8 of them were called in dollars. “
Source: Ambito
I am a 24-year-old writer and journalist who has been working in the news industry for the past two years. I write primarily about market news, so if you’re looking for insights into what’s going on in the stock market or economic indicators, you’ve come to the right place. I also dabble in writing articles on lifestyle trends and pop culture news.




