In mid-2024, some 155 taxes on human and legal persons. The breakdown is 46 national taxes, 25 provincial and 84 municipal “rates and contributions”. The photo shows that there is still a strong tax pressure in the country, despite the Government’s efforts to counteract this scheme.
The objective of the report is to have a measure of how many taxes per year an Argentine can pay, depending on their work structure, possession of goods and consumption. From the analysis of the 2024 tax legislation that arises from the Vademecum 2024, it was identified that depending on the consumption profiles proposed, people can pay at least 22 to 48 different taxes in the year. In the case of people who consume tobacco, they can pay from 25 to 51 different taxes a year.
The Iaraf study considered three different profiles, trying to encompass the different behaviors of Argentines. The criterion used is that of the existence of taxable event, fact being understood as everything that gives rise to the existence of a tax for a certain level of government. As an example, to facilitate understanding: the purchase of food and beverages (non-alcoholic) gives rise to the collection by the different state levels of at least 4 taxes, such as VAT and check tax at the state level. national, IIBB at the provincial level and TISH at the municipal level.
In Argentina there are three levels of government that seek to finance themselves: national, provincial and municipal level. Beyond the distinction of taxes by levels, some have the character of co-participating, that is, part of their Collection is distributed to the lower jurisdictional level. What did this study update reveal?
Three types of consumption profiles
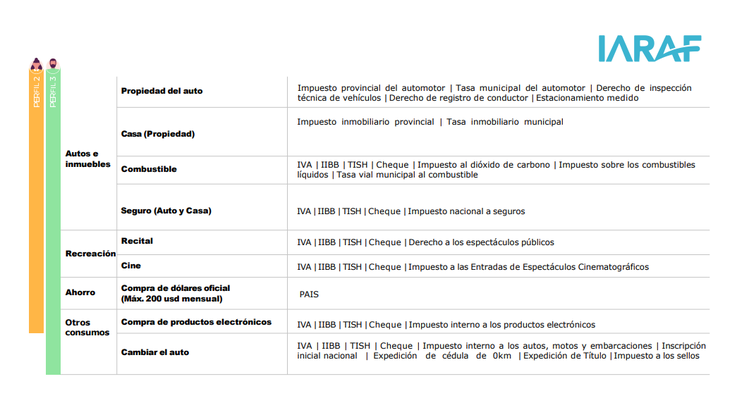
To carry out this study, three profiles are used, which differ according to income level and associated consumption. The person of profile 1with remuneration for their work, consumes food and drinks, acquires public services, contracts internet and entertainment on streaming platforms. To that of profile 2 It is added that he has a property (a house) and a car, for which, for example, he pays insurance. It is also considered that he attends a recital and a movie theater. And that buys dollars for hoarding. For him profile 3, A domestic flight for work purposes is added (a round-trip flight Córdoba-CABA is assumed), a trip abroad for vacation and the annual change of car for a “0km.” It is assumed that, for this profile, the sum of the values of the house and car exceed the non-taxable minimum to tax personal property
Tax pressure: how much taxes are paid for the consumption of an essential basket
At the beginning of the analysis, it is highlighted that the taxes paid for work in a dependent relationship are contributions to social security.
In the three profiles used for this analysis, the person has as I earn a salary in a dependency relationship, which he then uses to consume. For the calculation of taxes that affect consumption, all those that, regardless of whether payment corresponds to the seller, due to their transfer to the price, end up falling on the consumer are considered. The most common example is VAT.
Consumption is then discriminated by essential basket, which includes consumption with credit cards, food and beverages, public services, cell phones, internet and streaming platforms. From the list, it stands out that the largest amount of taxes in the same item is the payment of electricity, which includes everything from national to provincial and municipal taxes.
Screenshot 2024-11-03 131445.png
Screenshot 2024-11-03 131717.png
Screenshot 2024-11-03 131728.png
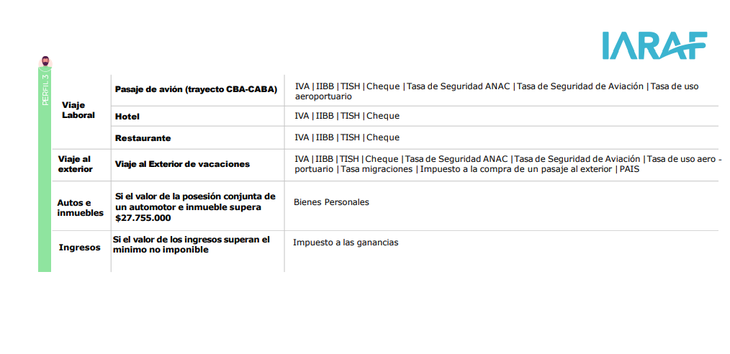
From the analysis it is concluded that the person identified with Profile 1 can pay at least 22 taxes different in the year. Meanwhile, people like Profile 2 can pay at least 37 taxes different. Lastly, the people of Profile 3 can pay at least 48 different taxes.
In the case of people who consume tobacco or its derivatives, the previous sum is increased by three taxes. In fact, a profile 1 smoker can pay at least 25 different taxes in the year, a profile 2 smoker at least 40 taxes and a profile 3 smoker at least 51 different taxes.
Conclusion of the analysis
The results of the study allow us to affirm that a person whose consumption is identified with what is assumed for profile 3, can pay at least 48 different taxes in the year. A 56% are of national origin, 15% are of provincial origin and 29% are of municipal origin. In the case of a smoker, the number of taxes amounts to 51 different taxes.
He The only tax that affects all defined consumption is the Value Added Tax. Second place is occupied by the gross income tax and the inspection, safety and hygiene fee (TISH), with 90%, 93.75% and 95% incidence per profile, respectively. This situation reflects that these three taxes are the ones that contribute the largest portion of the tax revenue obtained from consumption.
“Although this study does not analyze the tax burden that falls on the different profiles of people, the fact that 10 taxes concentrate 92% of the collectionallows us to infer that the Argentine tax framework presents excessive complexity, which can generate high administration costs for the different economic actors, including the treasury itself,” concluded the IARAF.
Source: Ambito




